Varicocele is a condition characterized by the enlargement of the veins within the scrotum. Call us to book an appointment with the best Vascular surgeon near you.
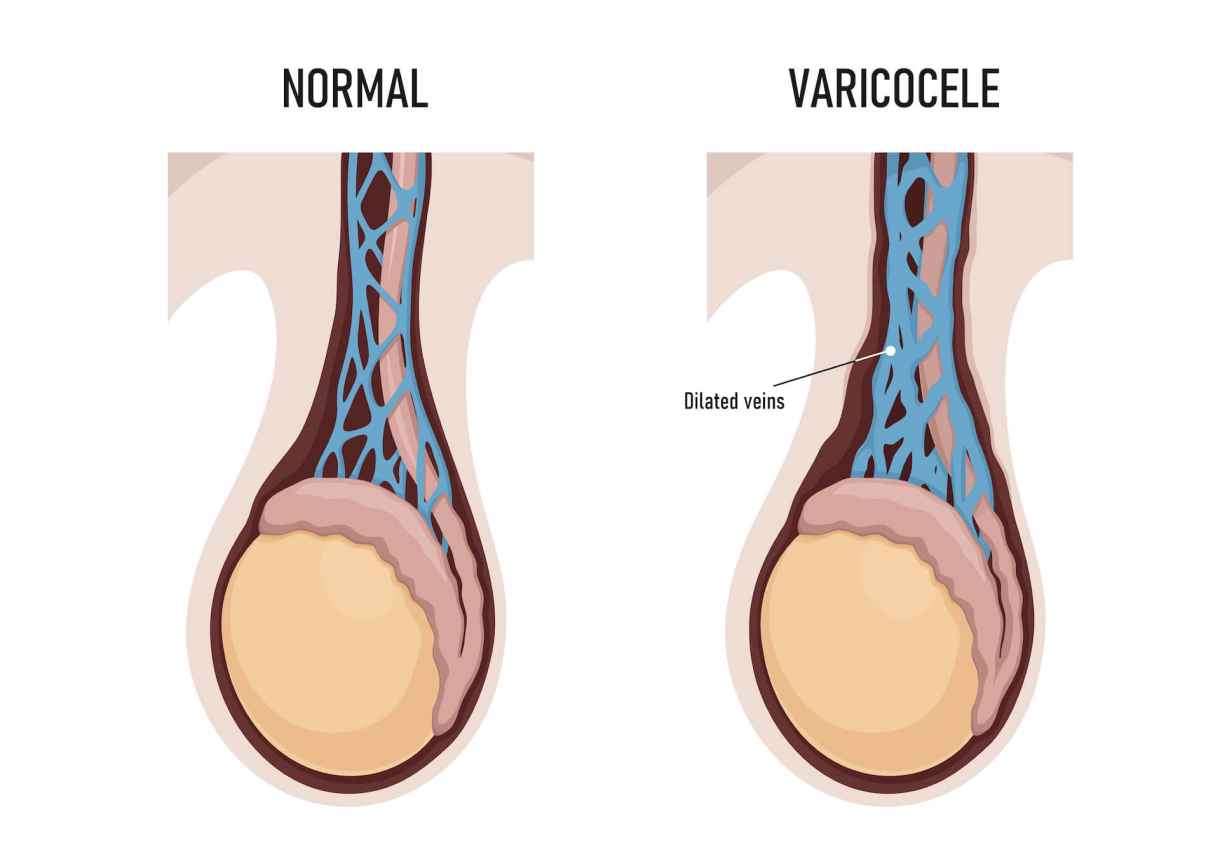
While some men may not experience any
symptoms, varicoceles can cause various signs that may prompt individuals to
seek treatment. These symptoms may include: 1. Swelling or lumps within the scrotum. 2. Dull or sharp pain, especially after
physical activity or prolonged sitting. 3. Discomfort or heaviness in the scrotum. 4. Fertility problems, such as reduced sperm
count or motility.

While some men may not experience any symptoms, varicoceles can cause various signs that may prompt individuals to seek treatment. These symptoms may include:
1. Swelling or lumps within the scrotum.
2. Dull or sharp pain, especially after physical activity or prolonged sitting.
3. Discomfort or heaviness in the scrotum.
4. Fertility problems, such as reduced sperm count or motility.
2. Varicocele Embolization: This non-surgical procedure involves blocking off the affected veins using a catheter and tiny coils or embolic agents. The procedure is typically guided by imaging techniques and is minimally invasive, offering a shorter recovery period compared to surgery.
2. Varicocele Embolization: This non-surgical procedure involves blocking off the affected veins using a catheter and tiny coils or embolic agents. The procedure is typically guided by imaging techniques and is minimally invasive, offering a shorter recovery period compared to surgery.
The main factors that contribute to varicocele development include: 1. Faulty Valves:
Inside the veins, there are tiny valves that help regulate blood flow
by preventing backward flow. If these valves become weak or faulty,
blood can accumulate in the veins, leading to their enlargement and the
formation of a varicocele. 2. Abnormal Vein Structure:
Some individuals may have a structural abnormality in the veins of the
scrotum, which increases the likelihood of developing varicoceles. These
structural differences can contribute to the dysfunction of the valves
and hinder proper blood flow. 3. Increased Blood Pressure:
High blood pressure within the testicular veins can also contribute to
varicocele formation. The increased pressure puts additional strain on
the veins, causing them to dilate and become varicose. 4. Genetic Predisposition:
There may be a genetic component to varicocele development, as it tends
to run in families. If a close family member, such as a father or
brother, has had a varicocele, the risk of developing one may be higher.
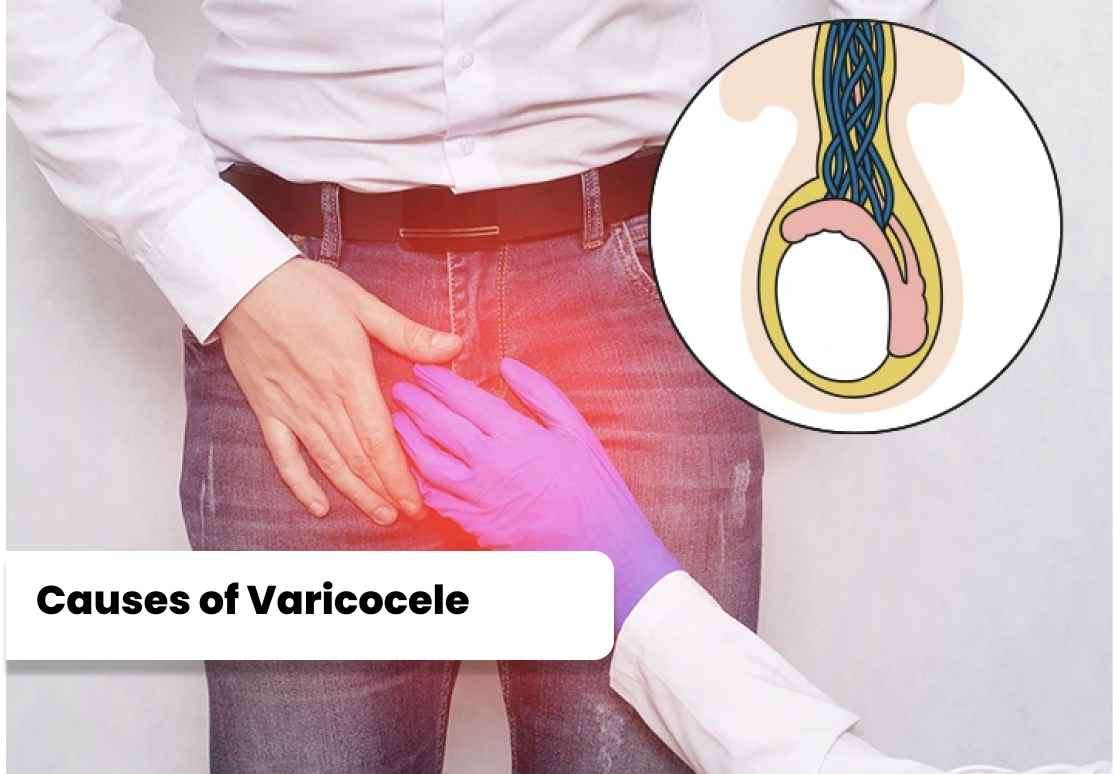
The main factors that contribute to varicocele development include:
1. Faulty Valves:
Inside the veins, there are tiny valves that help regulate blood flow
by preventing backward flow. If these valves become weak or faulty,
blood can accumulate in the veins, leading to their enlargement and the
formation of a varicocele.
2. Abnormal Vein Structure:
Some individuals may have a structural abnormality in the veins of the
scrotum, which increases the likelihood of developing varicoceles. These
structural differences can contribute to the dysfunction of the valves
and hinder proper blood flow.
3. Increased Blood Pressure: High blood pressure within the testicular veins can also contribute to varicocele formation. The increased pressure puts additional strain on the veins, causing them to dilate and become varicose.
4. Genetic Predisposition:
There may be a genetic component to varicocele development, as it tends
to run in families. If a close family member, such as a father or
brother, has had a varicocele, the risk of developing one may be higher.
a. Open Varicocelectomy: This traditional surgical approach involves making an incision in the lower abdomen or groin region to access and ligate the varicocele veins. b. Laparoscopic Varicocelectomy: In this minimally invasive procedure, specialized instruments and a small camera are inserted through tiny incisions in the abdomen. The surgeon uses these tools to locate and ligate the varicocele veins. c. Microsurgical Varicocelectomy: Considered the gold standard for varicocele treatment, this procedure utilizes an operating microscope to magnify the surgical field. The surgeon makes a small incision in the scrotum and precisely identifies and ligates the affected veins. Microsurgical varicocelectomy offers improved outcomes and lower recurrence rates. 2. Scrotal Varicocelectomy: This less common surgical technique involves making an incision directly on the scrotum to access and ligate the varicocele veins.
a. Open Varicocelectomy: This traditional surgical approach involves making an incision in the lower abdomen or groin region to access and ligate the varicocele veins.
b. Laparoscopic Varicocelectomy: In this minimally invasive procedure, specialized instruments and a small camera are inserted through tiny incisions in the abdomen. The surgeon uses these tools to locate and ligate the varicocele veins.
c. Microsurgical Varicocelectomy: Considered the gold standard for varicocele treatment, this procedure utilizes an operating microscope to magnify the surgical field. The surgeon makes a small incision in the scrotum and precisely identifies and ligates the affected veins. Microsurgical varicocelectomy offers improved outcomes and lower recurrence rates.
2. Scrotal Varicocelectomy: This less common surgical technique involves making an incision directly on the scrotum to access and ligate the varicocele veins.
The cost of varicocele treatment can vary depending on several factors, including the severity of the condition, the chosen treatment method, the healthcare facility, and the region or city in which the treatment is sought. Here is an approximate cost range for varicocele treatment in various Indian cities:
|
Serial No |
City |
Minimum Cost (INR) |
Average Cost (INR) |
|
1 |
Mumbai |
25,000 |
75,000 |
|
2 |
Delhi |
20,000 |
65,000 |
|
3 |
Bangalore |
18,000 |
60,000 |
|
4 |
Chennai |
15,000 |
55,000 |
|
5 |
Kolkata |
12,000 |
50,000 |
|
6 |
Hyderabad |
12,000 |
50,000 |
|
7 |
Pune |
10,000 |
45,000 |
|
8 |
Ahmedabad |
8,000 |
40,000 |
|
9 |
Jaipur |
8,000 |
40,000 |
|
10 |
Chandigarh |
7,000 |
35,000 |
|
11 |
Lucknow |
7,000 |
35,000 |
|
12 |
Indore |
6,000 |
30,000 |
|
13 |
Kochi |
6,000 |
30,000 |
|
14 |
Coimbatore |
5,000 |
25,000 |
|
15 |
Bhopal |
5,000 |
25,000 |
|
16 |
Nagpur |
4,000 |
20,000 |
|
17 |
Goa |
4,000 |
20,000 |
|
18 |
Mangalore |
3,500 |
18,000 |
|
19 |
Trivandrum |
3,500 |
18,000 |
|
20 |
Guwahati |
3,000 |
15,000 |
|
Serial No |
Hospital Name |
Address |
Contact Number |
|
1 |
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) |
Ansari Nagar, Aurobindo Marg, New Delhi - 110029 |
+91-11-26588500 |
|
2 |
Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER) |
Sector-12, Chandigarh - 160012 |
+91-172-2747585 |
|
3 |
Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences (SGPGIMS) |
Rae Bareli Road, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh - 226014 |
+91-522-2668700 |
|
4 |
JIPMER (Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research) |
Dhanvantari Nagar, Puducherry - 605006 |
+91-413-2296000 |
|
5 |
Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology (SCTIMST) |
Medical College P.O., Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala - 695011 |
+91-471-2524266 |
|
6 |
King George's Medical University (KGMU) |
Chowk, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh - 226003 |
+91-522-2257450 |
|
7 |
Nizam's Institute of Medical Sciences (NIMS) |
Punjagutta, Hyderabad, Telangana - 500082 |
+91-40-23489000 |
|
8 |
Government Medical College and Hospital (GMCH) |
Sector 32, Chandigarh - 160030 |
+91-172-2601023 |
|
9 |
Institute of Medical Sciences (IMS), Banaras Hindu University (BHU) |
Lanka, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh - 221005 |
+91-542-2367568 |
Please Wait..