A diabetic foot ulcer is an open sore or wound that occurs on the foot of a person with diabetes.
Call us to book an appointment with the best Vascular surgeon near you.
Diabetic foot ulcers are a common and serious complication that affects individuals living with diabetes. These ulcers are slow-healing wounds that can develop on the feet and lower extremities, often resulting from poor circulation and nerve damage. Without proper treatment, diabetic foot ulcers can lead to infection, gangrene, and even amputation. However, with the right approach and medical interventions, these ulcers can be effectively managed and treated.
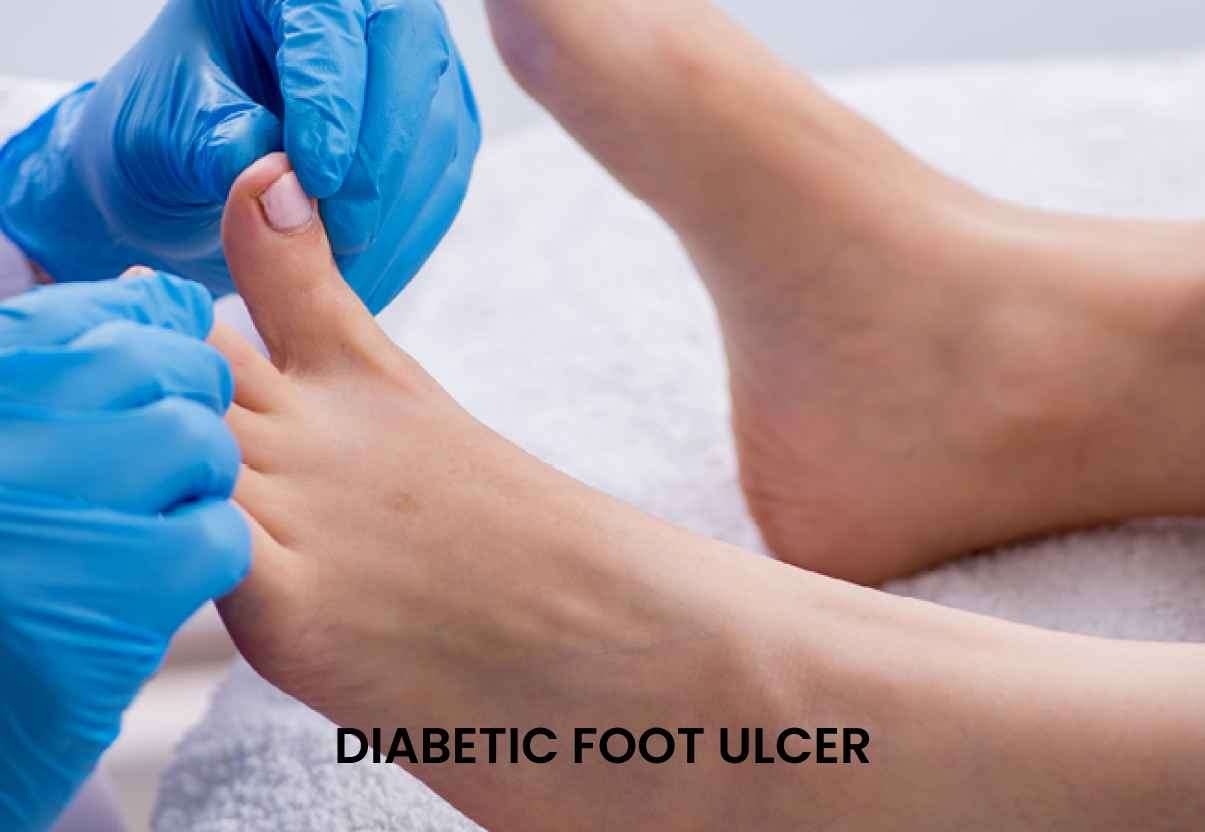
Diabetic foot ulcers are a common and serious complication that affects individuals living with diabetes. These ulcers are slow-healing wounds that can develop on the feet and lower extremities, often resulting from poor circulation and nerve damage. Without proper treatment, diabetic foot ulcers can lead to infection, gangrene, and even amputation. However, with the right approach and medical interventions, these ulcers can be effectively managed and treated.
The treatment of diabetic foot ulcers typically involves a combination of strategies, including: 1. Wound care: This involves cleaning the wound, removing dead tissue (debridement), and applying dressings to promote healing. 2. Offloading: Reducing pressure on the ulcer through the use of special footwear, casts, or other devices. 3. Infection control: If an infection is present, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat it. 4. Blood sugar control: Proper management of blood glucose levels is crucial for promoting healing and preventing complications. 5. Vascular intervention: In cases of impaired blood circulation, procedures such as angioplasty or bypass surgery may be considered. 6. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy:
This treatment involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber
to increase oxygen levels in the bloodstream, which can aid in wound
healing. 7. Biologic therapies: Some advanced therapies, such as growth factors or skin substitutes, may be used to enhance wound healing.
One of the fundamental aspects of diabetic
wound treatment is preventing and addressing infection. Diabetic patients are
more susceptible to infections due to compromised immune function and impaired
blood flow. Promptly treating any signs of infection is crucial to prevent
further complications. Antibiotics are commonly prescribed to combat bacterial
infections associated with diabetic foot ulcers. In severe cases, intravenous
antibiotics may be necessary to effectively control the infection.
When it comes to diabetic foot infection
treatment, a multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals
specializing in wound care, podiatry, and infectious diseases is often
recommended. Proper wound debridement is essential to remove dead tissue and
promote healing. Debridement can be performed through various methods, such as
surgical debridement, mechanical debridement using specialized dressings, or
enzymatic debridement using ointments containing enzymes that break down dead
tissue. Foot wound treatment also involves creating an
optimal environment for healing. Moist wound healing has been shown to be
effective in diabetic foot ulcer treatment. Special dressings and ointments can
be used to maintain a moist environment, which facilitates cell growth and
prevents the formation of dry, scaly skin that can impede healing. Silver-based
dressings are often used due to their antimicrobial properties, which help
prevent and control infections. In some cases, diabetic foot ulcers may
require surgical intervention. Diabetic foot surgery can be necessary when conservative
treatment methods fail to promote healing or when there is an underlying bone
infection (osteomyelitis). Surgical procedures aim to remove infected tissue,
improve blood flow, and relieve pressure on the affected area. Additionally,
surgical debridement can help remove necrotic tissue and promote wound healing. Alongside traditional wound care approaches,
there are various medications available for treatment of diabetic foot. Some
ointments, such as those containing growth factors or platelet-derived
products, can be applied to the ulcer site to stimulate healing. These
ointments aid in tissue regeneration and the formation of new blood vessels,
promoting the closure of the wound. Other topical medications, such as
antimicrobial creams or gels, may be prescribed to control infection and
prevent its spread. Managing diabetic foot ulcers also requires a
comprehensive approach to address the underlying factors contributing to their
development. Diabetic patients must maintain optimal blood sugar control to
promote healing and prevent further complications. Additionally, proper foot
care, including regular inspection, washing with mild soap and water, and
appropriate moisturization, is crucial to prevent the occurrence of wounds in
the first place.
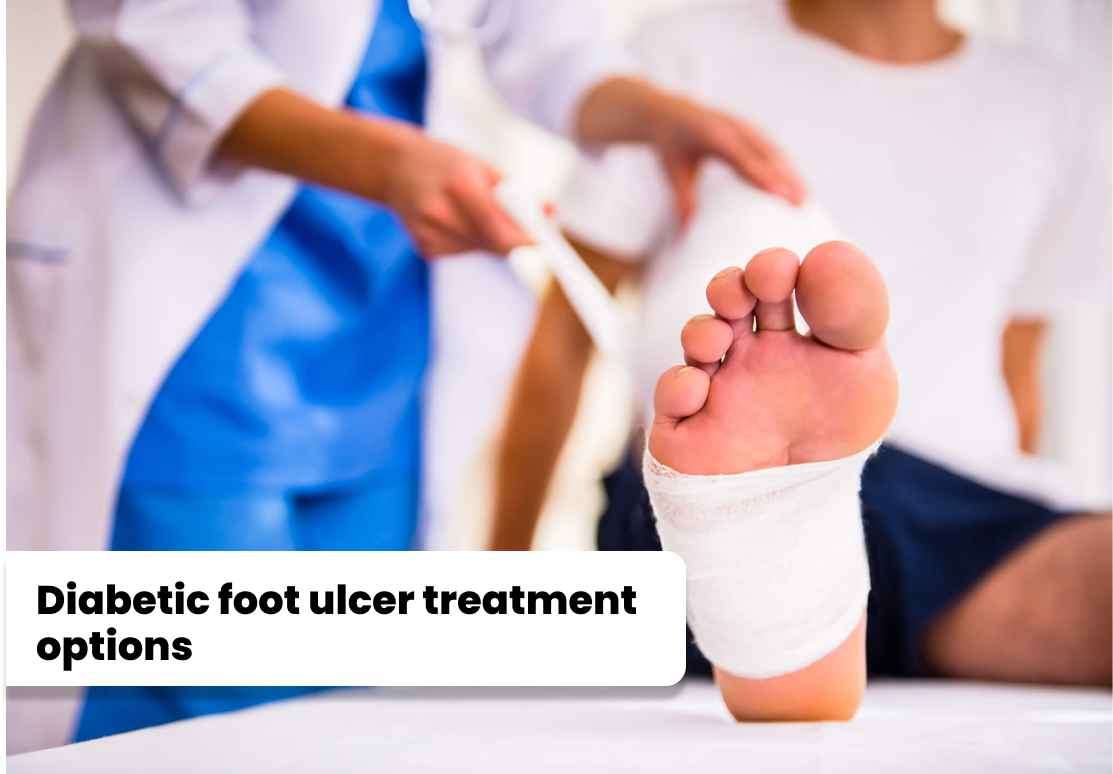
The treatment of diabetic foot ulcers typically involves a combination of strategies, including:
1. Wound care: This involves cleaning the wound, removing dead tissue (debridement), and applying dressings to promote healing.
2. Offloading: Reducing pressure on the ulcer through the use of special footwear, casts, or other devices.
3. Infection control: If an infection is present, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat it.
4. Blood sugar control: Proper management of blood glucose levels is crucial for promoting healing and preventing complications.
5. Vascular intervention: In cases of impaired blood circulation, procedures such as angioplasty or bypass surgery may be considered.
6. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy:
This treatment involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber
to increase oxygen levels in the bloodstream, which can aid in wound
healing.
7. Biologic therapies: Some advanced therapies, such as growth factors or skin substitutes, may be used to enhance wound healing.
One of the fundamental aspects of diabetic wound treatment is preventing and addressing infection. Diabetic patients are more susceptible to infections due to compromised immune function and impaired blood flow. Promptly treating any signs of infection is crucial to prevent further complications. Antibiotics are commonly prescribed to combat bacterial infections associated with diabetic foot ulcers. In severe cases, intravenous antibiotics may be necessary to effectively control the infection.
When it comes to diabetic foot infection treatment, a multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals specializing in wound care, podiatry, and infectious diseases is often recommended. Proper wound debridement is essential to remove dead tissue and promote healing. Debridement can be performed through various methods, such as surgical debridement, mechanical debridement using specialized dressings, or enzymatic debridement using ointments containing enzymes that break down dead tissue.
Foot wound treatment also involves creating an optimal environment for healing. Moist wound healing has been shown to be effective in diabetic foot ulcer treatment. Special dressings and ointments can be used to maintain a moist environment, which facilitates cell growth and prevents the formation of dry, scaly skin that can impede healing. Silver-based dressings are often used due to their antimicrobial properties, which help prevent and control infections.
In some cases, diabetic foot ulcers may require surgical intervention. Diabetic foot surgery can be necessary when conservative treatment methods fail to promote healing or when there is an underlying bone infection (osteomyelitis). Surgical procedures aim to remove infected tissue, improve blood flow, and relieve pressure on the affected area. Additionally, surgical debridement can help remove necrotic tissue and promote wound healing.
Alongside traditional wound care approaches, there are various medications available for treatment of diabetic foot. Some ointments, such as those containing growth factors or platelet-derived products, can be applied to the ulcer site to stimulate healing. These ointments aid in tissue regeneration and the formation of new blood vessels, promoting the closure of the wound. Other topical medications, such as antimicrobial creams or gels, may be prescribed to control infection and prevent its spread.
Managing diabetic foot ulcers also requires a comprehensive approach to address the underlying factors contributing to their development. Diabetic patients must maintain optimal blood sugar control to promote healing and prevent further complications. Additionally, proper foot care, including regular inspection, washing with mild soap and water, and appropriate moisturization, is crucial to prevent the occurrence of wounds in the first place.
Preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing diabetic foot ulcers. Some important preventive strategies include: 1. Proper foot care: Regularly inspecting the feet for any wounds or abnormalities and keeping the feet clean and moisturized. 2. Wearing appropriate footwear: Choosing shoes that fit well and provide adequate support, cushioning, and protection. 3. Managing blood sugar levels: Keeping blood glucose levels within the target range to minimize nerve and blood vessel damage. 4. Regular check-ups: Regularly visiting a healthcare provider to assess foot health and detect any early signs of ulcers or complications. 5. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: Following a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. 6. Education and self-care: Learning about diabetic foot care and adopting good self-care habits to prevent injuries and promote early detection of potential problems.
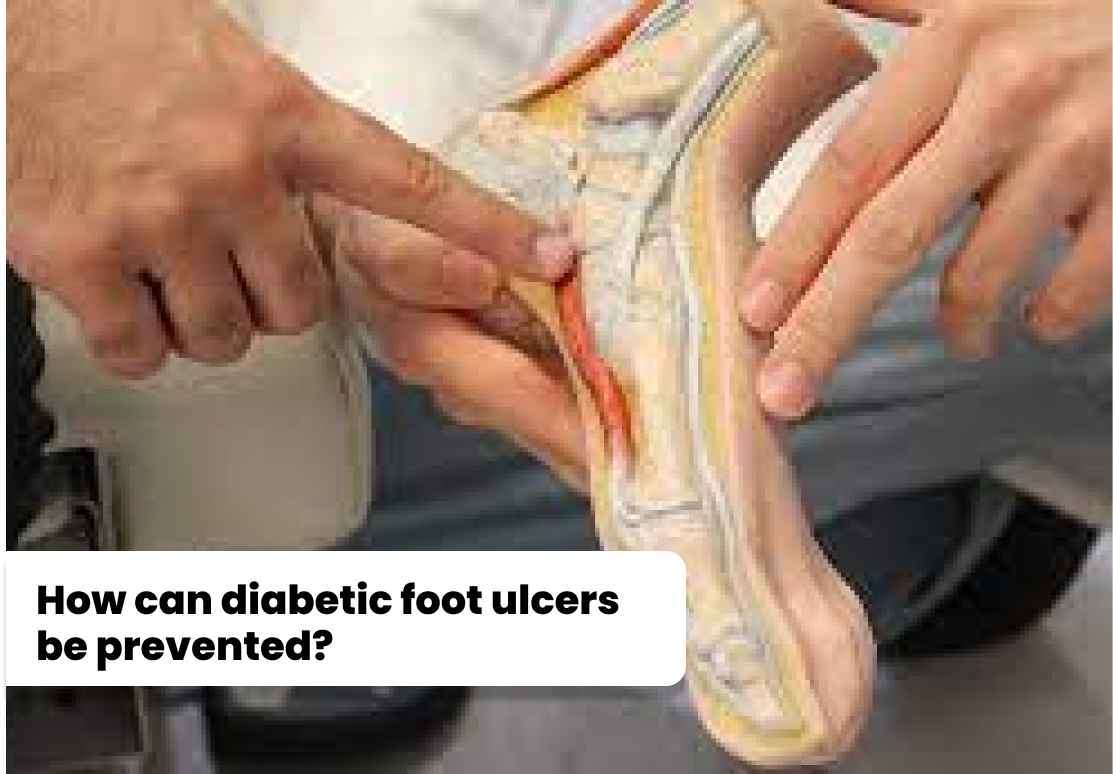
Preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing diabetic foot ulcers. Some important preventive strategies include:
1. Proper foot care: Regularly inspecting the feet for any wounds or abnormalities and keeping the feet clean and moisturized.
2. Wearing appropriate footwear: Choosing shoes that fit well and provide adequate support, cushioning, and protection.
3. Managing blood sugar levels: Keeping blood glucose levels within the target range to minimize nerve and blood vessel damage.
4. Regular check-ups: Regularly visiting a healthcare provider to assess foot health and detect any early signs of ulcers or complications.
5. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: Following a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
6. Education and self-care: Learning about diabetic foot care and adopting good self-care habits to prevent injuries and promote early detection of potential problems.
|
Serial No |
City |
Minimum Cost (INR) |
Average Cost (INR) |
|
1 |
Mumbai |
10,000 |
30,000 |
|
2 |
Delhi |
8,000 |
25,000 |
|
3 |
Bangalore |
7,000 |
22,000 |
|
4 |
Chennai |
6,000 |
20,000 |
|
5 |
Kolkata |
6,000 |
18,000 |
|
6 |
Hyderabad |
5,000 |
16,000 |
|
7 |
Pune |
5,000 |
15,000 |
|
8 |
Ahmedabad |
4,000 |
14,000 |
|
9 |
Jaipur |
4,000 |
13,000 |
|
10 |
Chandigarh |
3,000 |
12,000 |
|
11 |
Lucknow |
3,000 |
11,000 |
|
12 |
Indore |
2,500 |
10,000 |
|
13 |
Kochi |
2,500 |
9,000 |
|
14 |
Coimbatore |
2,000 |
8,000 |
|
15 |
Bhopal |
2,000 |
8,000 |
|
16 |
Nagpur |
2,000 |
7,000 |
|
17 |
Goa |
2,000 |
7,000 |
|
18 |
Mangalore |
1,500 |
6,000 |
|
19 |
Trivandrum |
1,500 |
6,000 |
|
20 |
Guwahati |
1,000 |
5,000 |
|
Serial No |
Hospital Name |
Address |
Contact Number |
|
1 |
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) |
Ansari Nagar, Aurobindo Marg, New Delhi - 110029 |
+91-11-26588500 |
|
2 |
Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER) |
Sector-12, Chandigarh - 160012 |
+91-172-2747585 |
|
3 |
Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences (SGPGIMS) |
Rae Bareli Road, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh - 226014 |
+91-522-2668700 |
|
4 |
JIPMER (Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research) |
Dhanvantari Nagar, Puducherry - 605006 |
+91-413-2296000 |
|
5 |
Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology (SCTIMST) |
Medical College P.O., Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala - 695011 |
+91-471-2524266 |
|
6 |
King George's Medical University (KGMU) |
Chowk, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh - 226003 |
+91-522-2257450 |
|
7 |
Nizam's Institute of Medical Sciences (NIMS) |
Punjagutta, Hyderabad, Telangana - 500082 |
+91-40-23489000 |
|
8 |
Government Medical College and Hospital (GMCH) |
Sector 32, Chandigarh - 160030 |
+91-172-2601023 |
|
9 |
Institute of Medical Sciences (IMS), Banaras Hindu University (BHU) |
Lanka, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh - 221005 |
+91-542-2367568 |
|
10 |
Osmania General Hospital |
Afzal Gunj, Hyderabad, Telangana - 500012 |
+91-40-24600146 |
Please Wait..