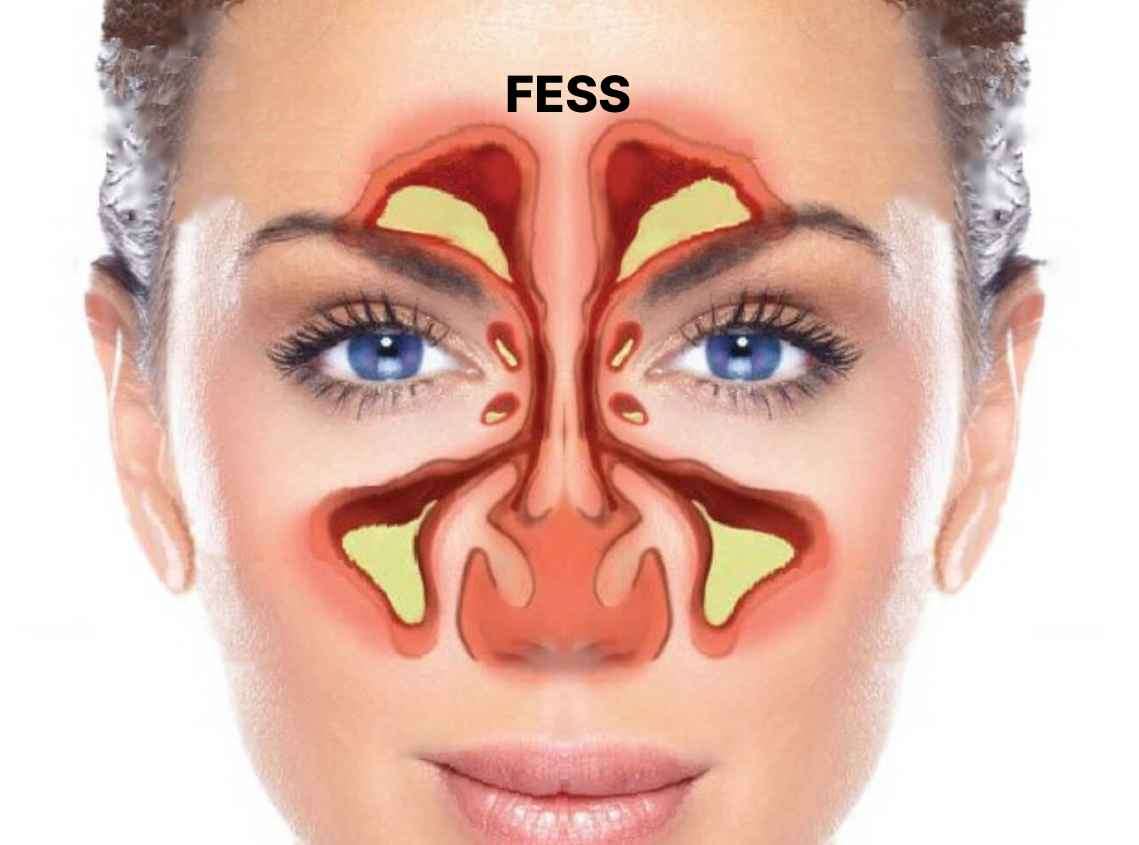
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS) is a surgical procedure performed to treat chronic sinusitis and other sinus-related conditions. Call us to book an appointment with the best Otolaryngologist-Ear, Nose, and Throat (ENT) specialist or a Sinus Surgeon near you.
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS) is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to treat chronic sinusitis and other sinus-related conditions. It is considered a significant advancement in sinus surgery as it allows for a thorough examination and treatment of the sinuses using endoscopes and specialized instruments. In this article, we will delve into the details of FESS, including its purpose, procedure, recovery, and potential benefits.
FESS aims to improve the drainage and ventilation of the sinuses by removing diseased tissue, polyps, and obstructions. Unlike traditional open sinus surgery, FESS is performed entirely through the nostrils without the need for external incisions, resulting in reduced post-operative discomfort, minimal scarring, and faster recovery.
Indications for FESS:
FESS sinus surgery is typically recommended for individuals with chronic or recurrent sinusitis that does not respond to medical treatments such as antibiotics, nasal sprays, or other conservative measures. It may also be indicated for certain nasal and sinus conditions, including nasal polyps, sinus tumors, fungal sinusitis, mucoceles, and structural abnormalities that affect sinus function.
Prior to the surgery, a thorough evaluation of the sinuses is performed using nasal endoscopy and radiographic imaging. During FESS, the patient is placed under general anesthesia, ensuring a pain-free and comfortable experience. The surgeon uses endoscopes, which are thin, flexible tubes with a light and camera, to visualize the sinus cavities. Specialized instruments are then used to remove diseased tissue, polyps, and other obstructions, while preserving healthy structures. FESS surgery steps: Anesthesia: The patient is placed under general anesthesia to ensure comfort and pain control throughout the surgery. Insertion of Endoscope: The surgeon inserts a thin, flexible endoscope through the nostril to visualize the nasal passages and sinus openings. The endoscope provides a magnified view of the sinus structures. Sinus Cavity Examination: The surgeon carefully examines the sinus cavities, looking for signs of inflammation, polyps, or other abnormalities. The endoscope helps guide the surgical instruments during the procedure. Removal of Diseased Tissue and Polyps: Using specialized instruments, the surgeon removes diseased tissue, polyps, and any obstructions that may be blocking the sinus passages. This step aims to improve sinus drainage and ventilation. Ethmoidectomy: If necessary, the surgeon may perform an ethmoidectomy, which involves removing the ethmoid sinus cells located between the eyes. This helps create more space and access for proper sinus drainage. Maxillary and Sphenoid Sinus Procedures: Depending on the patient's condition, the surgeon may address the maxillary and sphenoid sinuses using similar techniques. This may involve removing diseased tissue, enlarging sinus openings, or addressing specific issues within these sinuses. Septoplasty or Turbinate Reduction: If there are deviated nasal septum or enlarged turbinates contributing to sinus blockage, the surgeon may perform a septoplasty (straightening the nasal septum) or turbinate reduction (reducing the size of the turbinates) during the same procedure. Nasal Packing or Stents: After completing the necessary surgical steps, the surgeon may place dissolvable nasal packing or stents to support the healing process and reduce post-operative bleeding. Recovery and Follow-up: The patient is taken to a recovery area to allow for monitoring and initial recovery from anesthesia. In most cases, patients are discharged on the same day or the following day, but this can vary depending on the surgeon's preference and the patient's condition.
Prior to the surgery, a thorough evaluation of the sinuses is performed using nasal endoscopy and radiographic imaging. During FESS, the patient is placed under general anesthesia, ensuring a pain-free and comfortable experience. The surgeon uses endoscopes, which are thin, flexible tubes with a light and camera, to visualize the sinus cavities. Specialized instruments are then used to remove diseased tissue, polyps, and other obstructions, while preserving healthy structures. FESS surgery steps: Anesthesia: The patient is placed under general anesthesia to ensure comfort and pain control throughout the surgery. Insertion of Endoscope: The surgeon inserts a thin, flexible endoscope through the nostril to visualize the nasal passages and sinus openings. The endoscope provides a magnified view of the sinus structures. Sinus Cavity Examination: The surgeon carefully examines the sinus cavities, looking for signs of inflammation, polyps, or other abnormalities. The endoscope helps guide the surgical instruments during the procedure. Removal of Diseased Tissue and Polyps: Using specialized instruments, the surgeon removes diseased tissue, polyps, and any obstructions that may be blocking the sinus passages. This step aims to improve sinus drainage and ventilation. Ethmoidectomy: If necessary, the surgeon may perform an ethmoidectomy, which involves removing the ethmoid sinus cells located between the eyes. This helps create more space and access for proper sinus drainage. Maxillary and Sphenoid Sinus Procedures: Depending on the patient's condition, the surgeon may address the maxillary and sphenoid sinuses using similar techniques. This may involve removing diseased tissue, enlarging sinus openings, or addressing specific issues within these sinuses. Septoplasty or Turbinate Reduction: If there are deviated nasal septum or enlarged turbinates contributing to sinus blockage, the surgeon may perform a septoplasty (straightening the nasal septum) or turbinate reduction (reducing the size of the turbinates) during the same procedure. Nasal Packing or Stents: After completing the necessary surgical steps, the surgeon may place dissolvable nasal packing or stents to support the healing process and reduce post-operative bleeding. Recovery and Follow-up: The patient is taken to a recovery area to allow for monitoring and initial recovery from anesthesia. In most cases, patients are discharged on the same day or the following day, but this can vary depending on the surgeon's preference and the patient's condition.
FESS offers several advantages over traditional sinus surgery, including: Minimally invasive: The procedure is performed entirely through the nostrils, avoiding external incisions. Precise and thorough: The endoscopic visualization allows for a detailed examination of the sinuses, ensuring a comprehensive treatment. Shorter recovery time: Compared to open sinus surgery, FESS generally results in less post-operative pain, reduced hospital stays, and faster return to normal activities. Improved outcomes: By addressing the underlying causes of chronic sinusitis, FESS can lead to long-term relief, improved sinus function, and enhanced quality of life.
After FESS, patients are usually observed in a recovery area before being discharged on the same day or the following day. It is common to experience mild nasal congestion, drainage, and swelling for a few days. The surgeon may prescribe medications, such as nasal sprays or saline rinses, to promote healing and control inflammation. It is crucial to follow the post-operative instructions provided by the surgeon, including any activity restrictions, to ensure a smooth recovery.
Potential Risks and Complications of FESS:
While FESS is generally considered safe, as with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications. These may include bleeding, infection, damage to surrounding structures (such as the eyes or skull base), or recurrence of sinus problems. However, serious complications are rare, and the benefits of FESS often outweigh the risks in appropriately selected patients.
Follow-up and Long-term Management:
Regular follow-up visits with the surgeon are essential to monitor the healing process, evaluate treatment outcomes, and address any concerns. Long-term management of sinus health may involve ongoing medical treatments, such as nasal sprays, allergy management, or lifestyle modifications to reduce the risk of recurrence.
FESS offers several advantages over traditional sinus surgery, including:
Minimally invasive: The procedure is performed entirely through the nostrils, avoiding external incisions.
Precise and thorough: The endoscopic visualization allows for a detailed examination of the sinuses, ensuring a comprehensive treatment.
Shorter recovery time: Compared to open sinus surgery, FESS generally results in less post-operative pain, reduced hospital stays, and faster return to normal activities.
Improved outcomes: By addressing the underlying causes of chronic sinusitis, FESS can lead to long-term relief, improved sinus function, and enhanced quality of life.
After FESS, patients are usually observed in a recovery area before being discharged on the same day or the following day. It is common to experience mild nasal congestion, drainage, and swelling for a few days. The surgeon may prescribe medications, such as nasal sprays or saline rinses, to promote healing and control inflammation. It is crucial to follow the post-operative instructions provided by the surgeon, including any activity restrictions, to ensure a smooth recovery.
Potential Risks and Complications of FESS:
While FESS is generally considered safe, as with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications. These may include bleeding, infection, damage to surrounding structures (such as the eyes or skull base), or recurrence of sinus problems. However, serious complications are rare, and the benefits of FESS often outweigh the risks in appropriately selected patients.
Follow-up and Long-term Management:
Regular follow-up visits with the surgeon are essential to monitor the healing process, evaluate treatment outcomes, and address any concerns. Long-term management of sinus health may involve ongoing medical treatments, such as nasal sprays, allergy management, or lifestyle modifications to reduce the risk of recurrence.
City |
Average Cost (INR) |
Minimum Cost (INR) |
|
Delhi |
60,000 - 2,50,000 |
50,000 |
|
Mumbai |
50,000 - 3,00,000 |
40,000 |
|
Bangalore |
50,000 - 2,50,000 |
40,000 |
|
Chennai |
50,000 - 2,50,000 |
40,000 |
|
Hyderabad |
50,000 - 2,50,000 |
40,000 |
|
Kolkata |
50,000 - 2,50,000 |
40,000 |
|
Pune |
50,000 - 2,50,000 |
40,000 |
|
Ahmedabad |
40,000 - 2,00,000 |
30,000 |
|
Jaipur |
40,000 - 2,00,000 |
30,000 |
|
Chandigarh |
40,000 - 2,00,000 |
30,000 |
|
Lucknow |
40,000 - 2,00,000 |
30,000 |
|
Indore |
40,000 - 2,00,000 |
30,000 |
|
Kochi |
40,000 - 2,00,000 |
30,000 |
|
Bhopal |
40,000 - 2,00,000 |
30,000 |
|
Coimbatore |
40,000 - 2,00,000 |
30,000 |
|
Nagpur |
40,000 - 2,00,000 |
30,000 |
|
Ludhiana |
40,000 - 2,00,000 |
30,000 |
|
Goa |
40,000 - 2,00,000 |
30,000 |
|
Varanasi |
40,000 - 2,00,000 |
30,000 |
|
Surat |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Vadodara |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Patna |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Raipur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Ranchi |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Jamshedpur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Allahabad |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Bhopal |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Gorakhpur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Agra |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Varanasi |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Kanpur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Jodhpur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Rajkot |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Jabalpur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Jamnagar |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Dhanbad |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Patiala |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Meerut |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Salem |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Aligarh |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Bhilai |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Mangalore |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Kolhapur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Udaipur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Tirunelveli |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Jhansi |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Nanded |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Tirupati |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Gorakhpur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Dehradun |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Amravati |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Warangal |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Bikaner |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Guntur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Saharanpur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Shimla |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Muzaffarpur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Ajmer |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Bokaro |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Ujjain |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Kurnool |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Gulbarga |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Rohtak |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Durgapur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Bilaspur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Rourkela |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Jammu |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Mathura |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Ambala |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Dibrugarh |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Jalandhar |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Bhagalpur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Gwalior |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Thrissur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Nellore |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Raichur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Kadapa |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Belgaum |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Tiruppur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Bhavnagar |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Tiruvannamalai |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Puducherry |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Udupi |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Tiruchirappalli |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Rishikesh |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Alappuzha |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Pathankot |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Nizamabad |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Kottayam |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Karimnagar |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Thanjavur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Gaya |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Hospet |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Ambala |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Kakinada |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Bharatpur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Ongole |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Rewa |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Bhimavaram |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Eluru |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Proddatur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Nalgonda |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Guntakal |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Srikakulam |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Khammam |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Kadiri |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Chittoor |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Kottarakara |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Pathanamthitta |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Kharagpur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Bhimavaram |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Mirzapur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Pali |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Ratlam |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Haldwani |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Sambhal |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Raiganj |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Morbi |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Berhampur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Vellore |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Bhuj |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Dindigul |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Orai |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Bahraich |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Rewari |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Etawah |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Hoshiarpur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Chhindwara |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Chittorgarh |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Alwar |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Dhule |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Anantapur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Purnia |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Panipat |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Adilabad |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Katni |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Arrah |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Bardhaman |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Firozabad |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Khandwa |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Barasat |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Bidar |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Surendranagar |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Ratnagiri |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Saharsa |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Miryalaguda |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Gonda |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Jalandhar |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Dharwad |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Anand |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Kolar |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Baharampur |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Nandyal |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Thoothukudi |
40,000 - 80,000 |
30,000 |
|
Hospital Name |
Address |
Contact Number |
|
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) |
Ansari Nagar, New Delhi - 110029 |
+91-11-26588500 |
|
Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER) |
Sector-12, Chandigarh - 160012 |
+91-172-2746018 |
|
Sanjay Gandhi Post-Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences (SGPGIMS) |
Raebareli Road, Lucknow - 226014 |
+91-522-2494000 |
|
Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research (JIPMER) |
Dhanvantri Nagar, Puducherry - 605006 |
+91-413-2296562 |
|
Christian Medical College (CMC) Vellore |
Ida Scudder Road, Vellore - 632004 |
+91-416-2281000 |
|
King George's Medical University (KGMU) |
Chowk, Lucknow - 226003 |
+91-522-2257450 |
|
Sawai Man Singh Medical College (SMS Medical College) |
JLN Marg, Jaipur - 302004 |
+91-141-2518380 |
|
Government Medical College and Hospital (GMCH) Chandigarh |
Sector 32, Chandigarh - 160030 |
+91-172-2601023 |
|
Madras Medical College (MMC) |
Park Town, Chennai - 600003 |
+91-44-25305301 |
|
Lok Nayak Jai Prakash Narayan Hospital (LNJP) |
Jawaharlal Nehru Marg, Delhi - 110002 |
+91-11-23232400 |
Please Wait..