The treatment options for ectopic pregnancy depend on the size of the ectopic pregnancy, the presence or absence of symptoms, the location of the pregnancy, and the overall health of the individual. Call us to book an appointment with the best Obstetrician-Gynecologists (OB-GYNs) near you.
Ectopic pregnancy also called fallopian tube pregnancy is a potentially life-threatening condition where a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, typically in the fallopian tube. As the pregnancy progresses, it can cause severe complications and requires immediate medical intervention. In this article, we will delve into the various treatment options available for ectopic pregnancy, highlighting their benefits, considerations, and implications for women's health.
Ectopic Pregnancy causes:
Ectopic pregnancy can be caused by various factors, including:
Damaged fallopian tubes: Conditions such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), previous pelvic surgery, or certain sexually transmitted infections can lead to scarring or damage in the fallopian tubes, increasing the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Hormonal imbalances: Abnormal hormone levels or hormonal conditions can affect the movement of the fertilized egg through the fallopian tubes, increasing the chances of ectopic implantation.
Abnormalities in the fallopian tubes: Structural abnormalities in the fallopian tubes, either congenital or acquired, can disrupt the normal path of the fertilized egg.
Early signs of ectopic pregnancy may resemble those of a normal pregnancy, including a missed period, breast tenderness, and nausea. However, as the pregnancy progresses, specific symptoms of ectopic pregnancy may arise, such as: Abdominal pain: Sharp or cramp-like pain in the lower abdomen or pelvic area is a common symptom. The pain may become severe and persistent. Vaginal bleeding: Light to heavy vaginal bleeding may occur, often different from the usual menstrual bleeding. Shoulder pain: In some cases, shoulder pain can develop as a result of internal bleeding irritating the diaphragm. Weakness and dizziness: Internal bleeding can lead to a drop in blood pressure, causing weakness and dizziness.
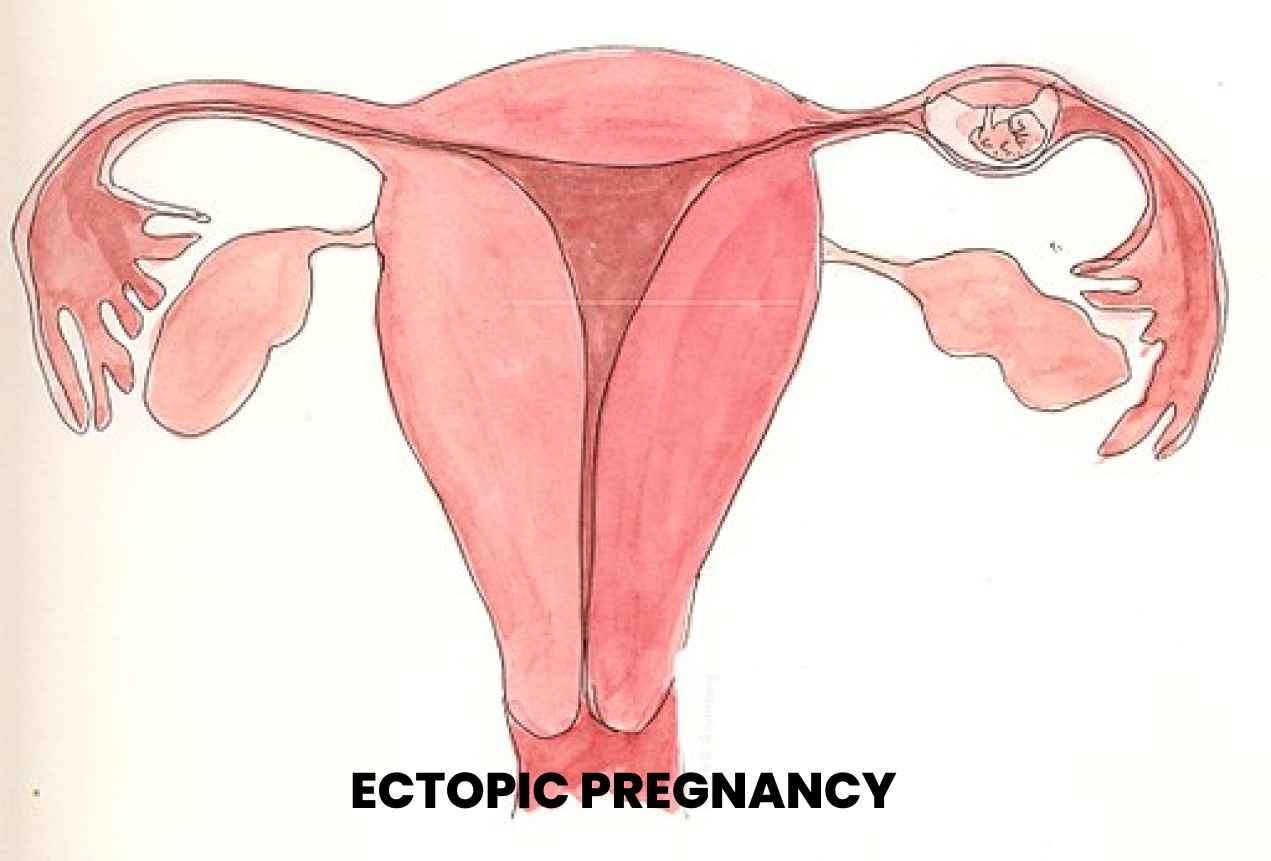
Early signs of ectopic pregnancy may resemble those of a normal pregnancy, including a missed period, breast tenderness, and nausea. However, as the pregnancy progresses, specific symptoms of ectopic pregnancy may arise, such as:
Abdominal pain: Sharp or cramp-like pain in the lower abdomen or pelvic area is a common symptom. The pain may become severe and persistent.
Vaginal bleeding: Light to heavy vaginal bleeding may occur, often different from the usual menstrual bleeding.
Shoulder pain: In some cases, shoulder pain can develop as a result of internal bleeding irritating the diaphragm.
Weakness and dizziness: Internal bleeding can lead to a drop in blood pressure, causing weakness and dizziness.
If ectopic pregnancy is suspected, prompt medical attention is crucial. The following diagnostic methods and treatment options are commonly used: Pelvic examination: A physical examination helps identify any signs of tenderness or abnormality in the reproductive organs. Ectopic Pregnancy Ultrasound: Transvaginal ultrasound is a key diagnostic tool for confirming ectopic pregnancy by visualizing the location of the gestational sac. Blood Tests: Quantitative human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) blood tests help monitor the levels of pregnancy hormone to detect abnormalities. Medication: In certain cases of early ectopic pregnancy and stable conditions, medication such as methotrexate may be used to stop the growth of the pregnancy tissue and avoid surgical intervention. Surgery: Surgical intervention is often necessary for ectopic pregnancies that have ruptured or are at risk of rupturing. Laparoscopic surgery or, in severe cases, open abdominal surgery may be performed to remove the ectopic pregnancy while preserving the fallopian tube.
If ectopic pregnancy is suspected, prompt medical attention is crucial. The following diagnostic methods and treatment options are commonly used:
Pelvic examination: A physical examination helps identify any signs of tenderness or abnormality in the reproductive organs.
Ectopic Pregnancy Ultrasound: Transvaginal ultrasound is a key diagnostic tool for confirming ectopic pregnancy by visualizing the location of the gestational sac.
Blood Tests: Quantitative human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) blood tests help monitor the levels of pregnancy hormone to detect abnormalities.
Medication: In certain cases of early ectopic pregnancy and stable conditions, medication such as methotrexate may be used to stop the growth of the pregnancy tissue and avoid surgical intervention.
Surgery: Surgical intervention is often necessary for ectopic pregnancies that have ruptured or are at risk of rupturing. Laparoscopic surgery or, in severe cases, open abdominal surgery may be performed to remove the ectopic pregnancy while preserving the fallopian tube.
Surgery is often necessary when ectopic pregnancies pose a significant risk to a woman's health or have already caused complications. There are two primary surgical approaches: a. Laparoscopic Surgery: This minimally invasive procedure involves making small incisions in the abdomen and using a laparoscope to remove the ectopic pregnancy. The surgeon can also repair or remove a damaged fallopian tube if necessary. Laparoscopic surgery offers faster recovery times, reduced scarring, and shorter hospital stays compared to open abdominal surgery. b. Open Abdominal Surgery: In cases of severe rupture or extensive internal bleeding, open abdominal surgery, also known as laparotomy, may be required. This procedure involves making a larger incision in the abdomen to access and remove the ectopic pregnancy. Laparotomy is associated with a longer recovery period and a higher risk of complications but may be necessary in certain emergency situations. Dealing with an ectopic pregnancy can be emotionally challenging for women and their partners. The loss of a pregnancy and the potential impact on fertility may cause distress. It is essential to provide emotional support, counseling, and resources to help individuals cope with the physical and emotional aspects of ectopic pregnancy and to address any concerns or anxieties. Fertility Considerations: Ectopic pregnancies can affect future fertility, particularly if surgical intervention requires the removal of a fallopian tube. However, many women who have had an ectopic pregnancy go on to have successful pregnancies in the future. Fertility counseling and discussions with healthcare providers are crucial for understanding individual circumstances and exploring options for conception and family planning. Risks and Outlook: Ectopic pregnancy poses significant risks to a woman's health, including the potential for severe internal bleeding and damage to the reproductive organs. Early detection and intervention are crucial to prevent complications. The prognosis for future pregnancies after an ectopic pregnancy varies depending on individual circumstances and the extent of any damage to the fallopian tubes or other reproductive organs.
Surgery is often necessary when ectopic pregnancies pose a significant risk to a woman's health or have already caused complications. There are two primary surgical approaches:
a. Laparoscopic Surgery: This minimally invasive procedure involves making small incisions in the abdomen and using a laparoscope to remove the ectopic pregnancy. The surgeon can also repair or remove a damaged fallopian tube if necessary. Laparoscopic surgery offers faster recovery times, reduced scarring, and shorter hospital stays compared to open abdominal surgery.
b. Open Abdominal Surgery: In cases of severe rupture or extensive internal bleeding, open abdominal surgery, also known as laparotomy, may be required. This procedure involves making a larger incision in the abdomen to access and remove the ectopic pregnancy. Laparotomy is associated with a longer recovery period and a higher risk of complications but may be necessary in certain emergency situations.
Dealing with an ectopic pregnancy can be emotionally challenging for women and their partners. The loss of a pregnancy and the potential impact on fertility may cause distress. It is essential to provide emotional support, counseling, and resources to help individuals cope with the physical and emotional aspects of ectopic pregnancy and to address any concerns or anxieties.
Fertility Considerations:
Ectopic pregnancies can affect future fertility, particularly if surgical intervention requires the removal of a fallopian tube. However, many women who have had an ectopic pregnancy go on to have successful pregnancies in the future. Fertility counseling and discussions with healthcare providers are crucial for understanding individual circumstances and exploring options for conception and family planning.
Risks and Outlook:
Ectopic pregnancy poses significant risks to a woman's health, including the potential for severe internal bleeding and damage to the reproductive organs. Early detection and intervention are crucial to prevent complications. The prognosis for future pregnancies after an ectopic pregnancy varies depending on individual circumstances and the extent of any damage to the fallopian tubes or other reproductive organs.
Please Wait..