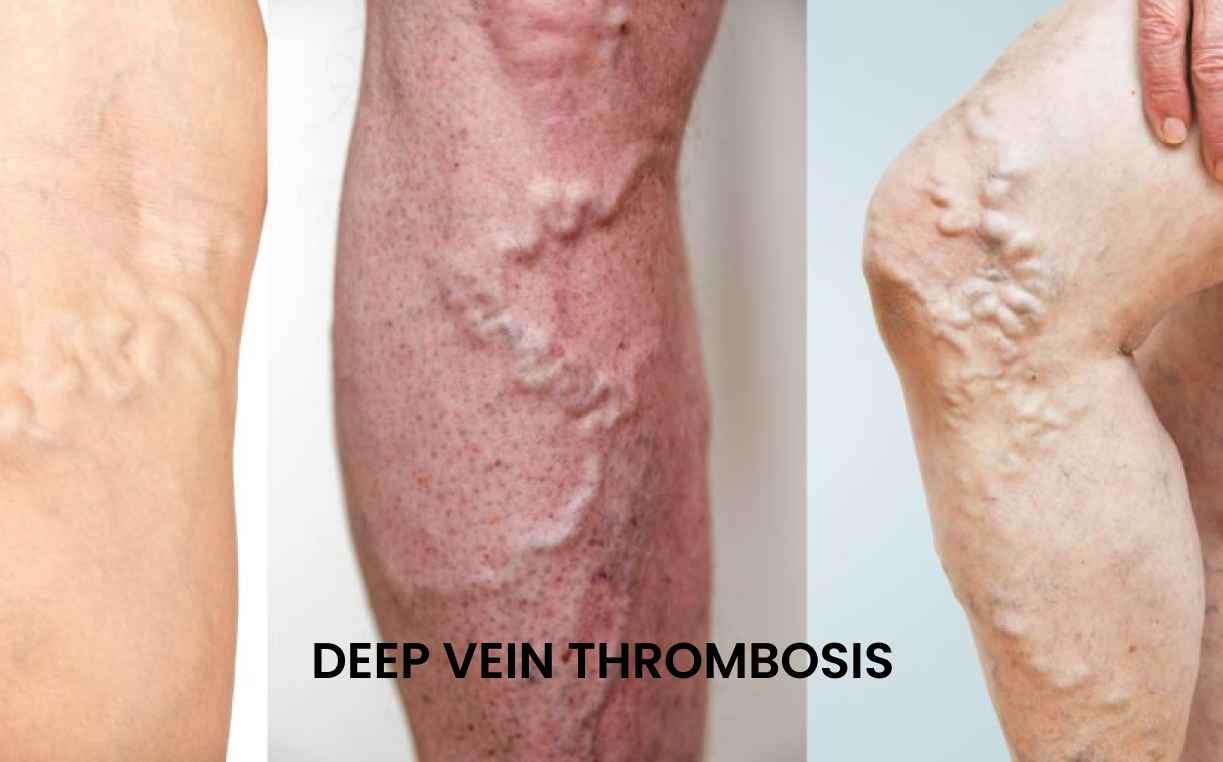
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition in which a blood clot forms in
a deep vein, usually in the leg. It is a serious condition that
requires prompt medical attention. If left untreated, DVT can lead to
complications such as pulmonary embolism (when a clot travels to the
lungs) or post-thrombotic syndrome (chronic pain and swelling in the
affected area).
Call us to book an appointment with the best Vascular surgeon near you.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious
medical condition characterized by the formation of blood clots in the deep
veins, most commonly in the legs. If left untreated, these clots can lead to
complications such as pulmonary embolism, which is a potentially
life-threatening condition. Effective DVT treatment is crucial to prevent
complications and manage the condition.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious
medical condition characterized by the formation of blood clots in the deep
veins, most commonly in the legs. If left untreated, these clots can lead to
complications such as pulmonary embolism, which is a potentially
life-threatening condition. Effective DVT treatment is crucial to prevent
complications and manage the condition.
 Management.jpg)
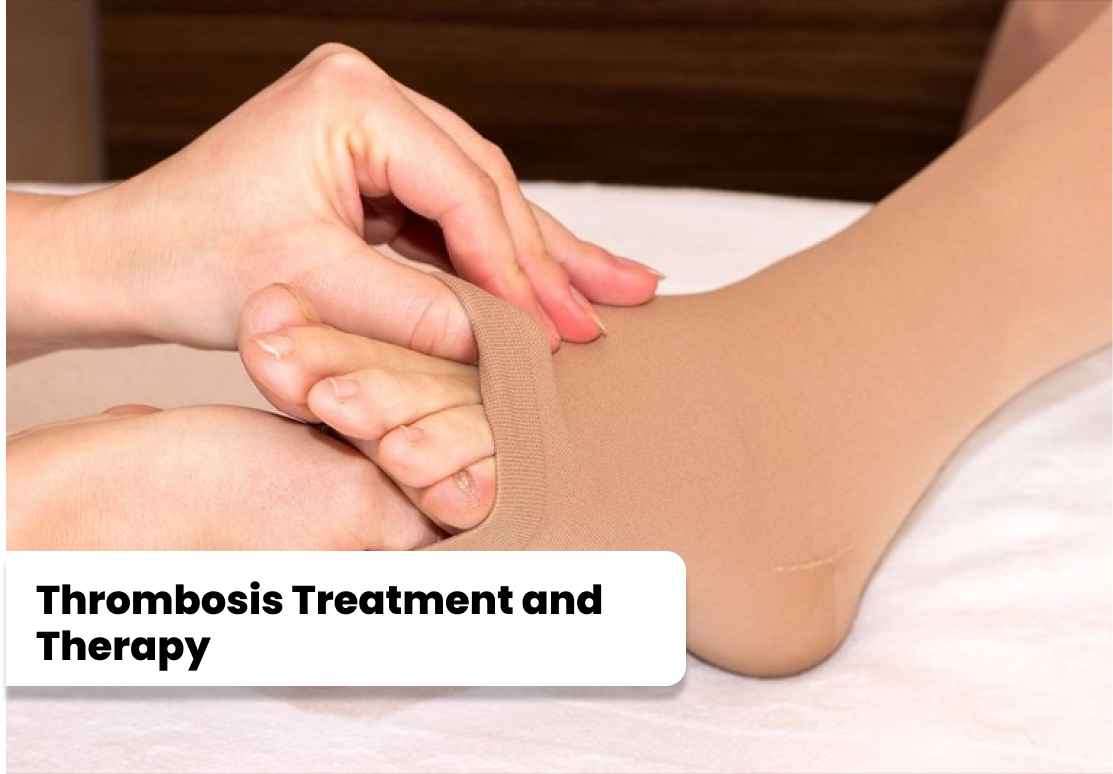
Anticoagulant Therapy: Anticoagulant medications, such as heparin and
warfarin, are commonly prescribed to prevent blood clots from enlarging and to
reduce the risk of new clots forming. These medications work by inhibiting the
clotting factors in the blood, thus preventing the formation of additional
clots. The duration of anticoagulant therapy varies depending on individual
circumstances.
DVT Surgery:In certain cases, DVT surgery may be necessary
to remove a clot or to alleviate vein blockage. Thrombectomy is a surgical
procedure that involves the removal of the clot from the affected vein. This
intervention is typically considered when the clot is extensive, causing severe
symptoms, or posing a significant risk of complications. Venous Thromboembolism Treatment: Venous thromboembolism (VTE) refers to the
formation of blood clots in the veins. It includes conditions such as DVT and
pulmonary embolism. The treatment approach for VTE usually involves
anticoagulant therapy, which helps prevent the clot from enlarging and breaking
off into the lungs. Venous Sinus Thrombosis Treatment: Venous sinus thrombosis is a rare form of
blood clotting disorder that occurs in the veins draining blood from the brain.
The treatment for venous sinus thrombosis often involves anticoagulant therapy,
sometimes combined with other interventions, such as endovascular procedures,
to restore normal blood flow. Acute DVT Treatment: Acute DVT refers to a recent or sudden onset
of DVT. The immediate goal of acute DVT treatment is to prevent the clot from
growing and to minimize the risk of complications. Anticoagulant therapy is the
primary treatment for acute DVT, and in severe cases, thrombolytic therapy may
be considered to dissolve the clot more rapidly. Artery Thrombosis Treatment: Arterial thrombosis, which occurs in the
arteries, is a separate condition from DVT. However, it is also a serious condition
that requires prompt medical attention. Treatment for artery thrombosis
typically involves antiplatelet medications, such as aspirin or clopidogrel,
and in some cases, surgical interventions like angioplasty or bypass surgery.
Anticoagulant Therapy: Anticoagulant medications, such as heparin and warfarin, are commonly prescribed to prevent blood clots from enlarging and to reduce the risk of new clots forming. These medications work by inhibiting the clotting factors in the blood, thus preventing the formation of additional clots. The duration of anticoagulant therapy varies depending on individual circumstances.
DVT Surgery:In certain cases, DVT surgery may be necessary to remove a clot or to alleviate vein blockage. Thrombectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the clot from the affected vein. This intervention is typically considered when the clot is extensive, causing severe symptoms, or posing a significant risk of complications.
Venous Thromboembolism Treatment: Venous thromboembolism (VTE) refers to the formation of blood clots in the veins. It includes conditions such as DVT and pulmonary embolism. The treatment approach for VTE usually involves anticoagulant therapy, which helps prevent the clot from enlarging and breaking off into the lungs.
Venous Sinus Thrombosis Treatment: Venous sinus thrombosis is a rare form of blood clotting disorder that occurs in the veins draining blood from the brain. The treatment for venous sinus thrombosis often involves anticoagulant therapy, sometimes combined with other interventions, such as endovascular procedures, to restore normal blood flow.
Acute DVT Treatment: Acute DVT refers to a recent or sudden onset of DVT. The immediate goal of acute DVT treatment is to prevent the clot from growing and to minimize the risk of complications. Anticoagulant therapy is the primary treatment for acute DVT, and in severe cases, thrombolytic therapy may be considered to dissolve the clot more rapidly.
Artery Thrombosis Treatment: Arterial thrombosis, which occurs in the arteries, is a separate condition from DVT. However, it is also a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention. Treatment for artery thrombosis typically involves antiplatelet medications, such as aspirin or clopidogrel, and in some cases, surgical interventions like angioplasty or bypass surgery.

The cost of treating Deep Vein Thrombosis
(DVT) can vary depending on several factors, including the severity of the
condition, the chosen treatment method, the duration of treatment required, the
healthcare facility, and the region or city in which the treatment is sought.
Here is an approximate cost range for DVT treatment in various Indian cities:
|
Serial No |
City |
Minimum Cost (INR) |
Average Cost (INR) |
|
1 |
Mumbai |
20,000 |
70,000 |
|
2 |
Delhi |
18,000 |
60,000 |
|
3 |
Bangalore |
15,000 |
50,000 |
|
4 |
Chennai |
14,000 |
45,000 |
|
5 |
Kolkata |
12,000 |
40,000 |
|
6 |
Hyderabad |
12,000 |
40,000 |
|
7 |
Pune |
10,000 |
35,000 |
|
8 |
Ahmedabad |
9,000 |
30,000 |
|
9 |
Jaipur |
8,000 |
28,000 |
|
10 |
Chandigarh |
7,000 |
25,000 |
|
11 |
Lucknow |
7,000 |
25,000 |
|
12 |
Indore |
6,000 |
22,000 |
|
13 |
Kochi |
6,000 |
22,000 |
|
14 |
Coimbatore |
5,000 |
20,000 |
|
15 |
Bhopal |
5,000 |
20,000 |
|
16 |
Nagpur |
4,000 |
18,000 |
|
17 |
Goa |
4,000 |
18,000 |
|
18 |
Mangalore |
3,500 |
15,000 |
|
19 |
Trivandrum |
3,500 |
15,000 |
|
20 |
Guwahati |
3,000 |
12,000 |
|
Serial No |
Hospital Name |
Address |
Contact Number |
|
1 |
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) |
Ansari Nagar, Aurobindo Marg, New Delhi - 110029 |
+91-11-26588500 |
|
2 |
Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER) |
Sector-12, Chandigarh - 160012 |
+91-172-2747585 |
|
3 |
Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences (SGPGIMS) |
Rae Bareli Road, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh - 226014 |
+91-522-2668700 |
|
4 |
JIPMER (Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research) |
Dhanvantari Nagar, Puducherry - 605006 |
+91-413-2296000 |
|
5 |
Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology (SCTIMST) |
Medical College P.O., Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala - 695011 |
+91-471-2524266 |
|
6 |
King George's Medical University (KGMU) |
Chowk, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh - 226003 |
+91-522-2257450 |
|
7 |
Nizam's Institute of Medical Sciences (NIMS) |
Punjagutta, Hyderabad, Telangana - 500082 |
+91-40-23489000 |
|
8 |
Government Medical College and Hospital (GMCH) |
Sector 32, Chandigarh - 160030 |
+91-172-2601023 |
|
9 |
Institute of Medical Sciences (IMS), Banaras Hindu University (BHU) |
Lanka, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh - 221005 |
+91-542-2367568 |
|
10 |
Osmania General Hospital |
Afzal Gunj, Hyderabad, Telangana - 500012 |
+91-40-24600146 |
Please Wait..