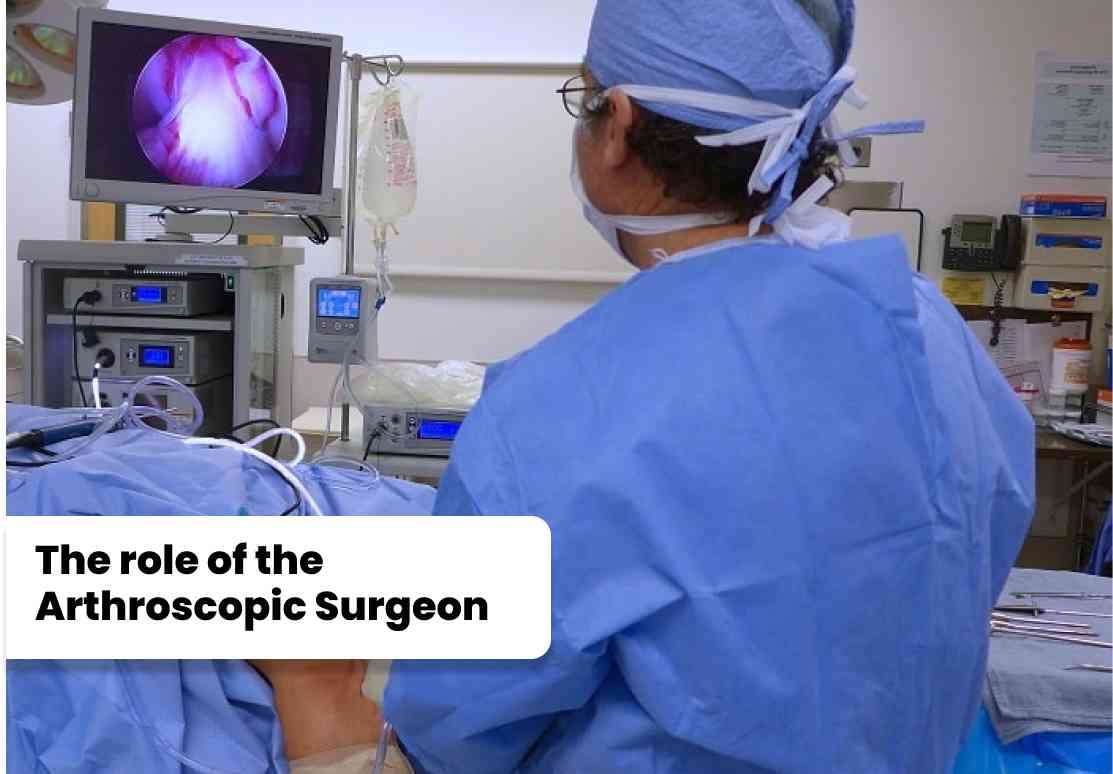
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that allows
doctors to visualize, diagnose, and treat problems inside a joint. It
involves the use of an arthroscope, which is a small, flexible
instrument equipped with a light source and a camera that can be
inserted through small incisions in the skin.
Call us to book a appointment with the best Ortho specialist near you.
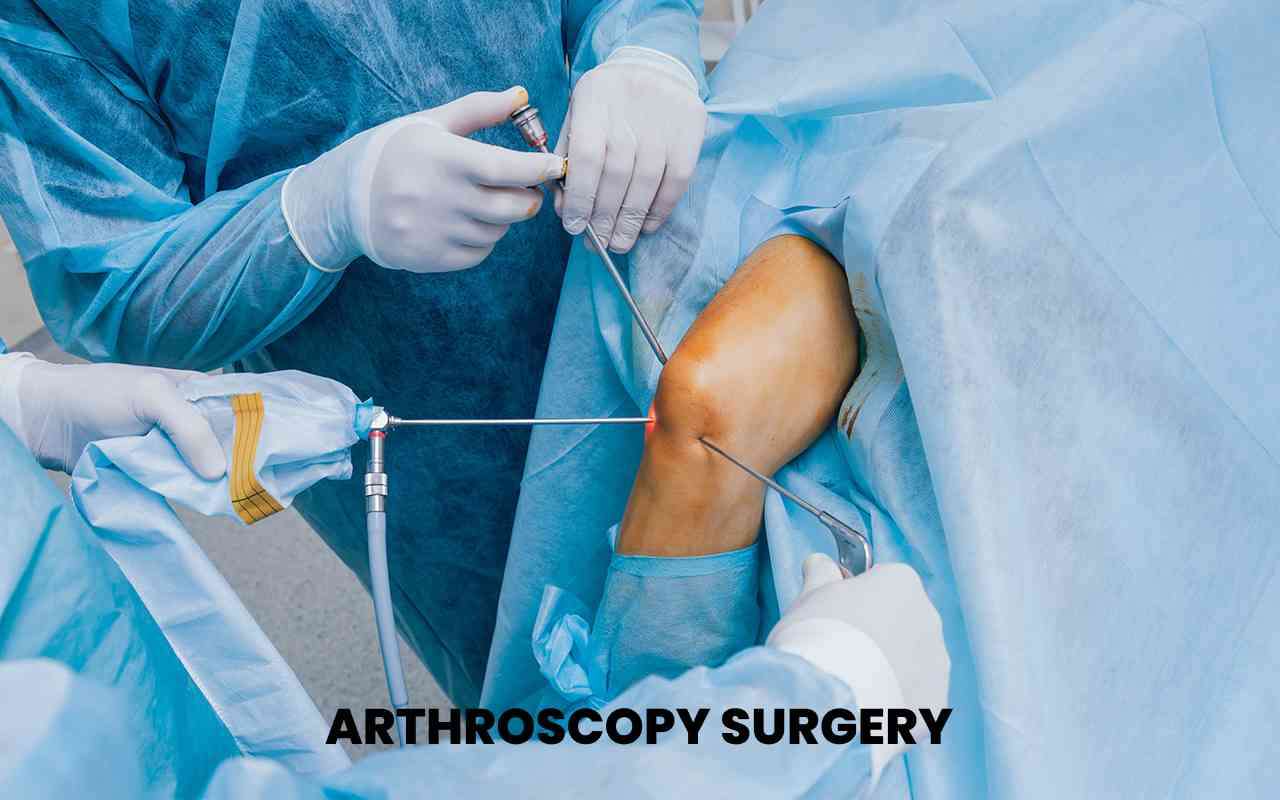

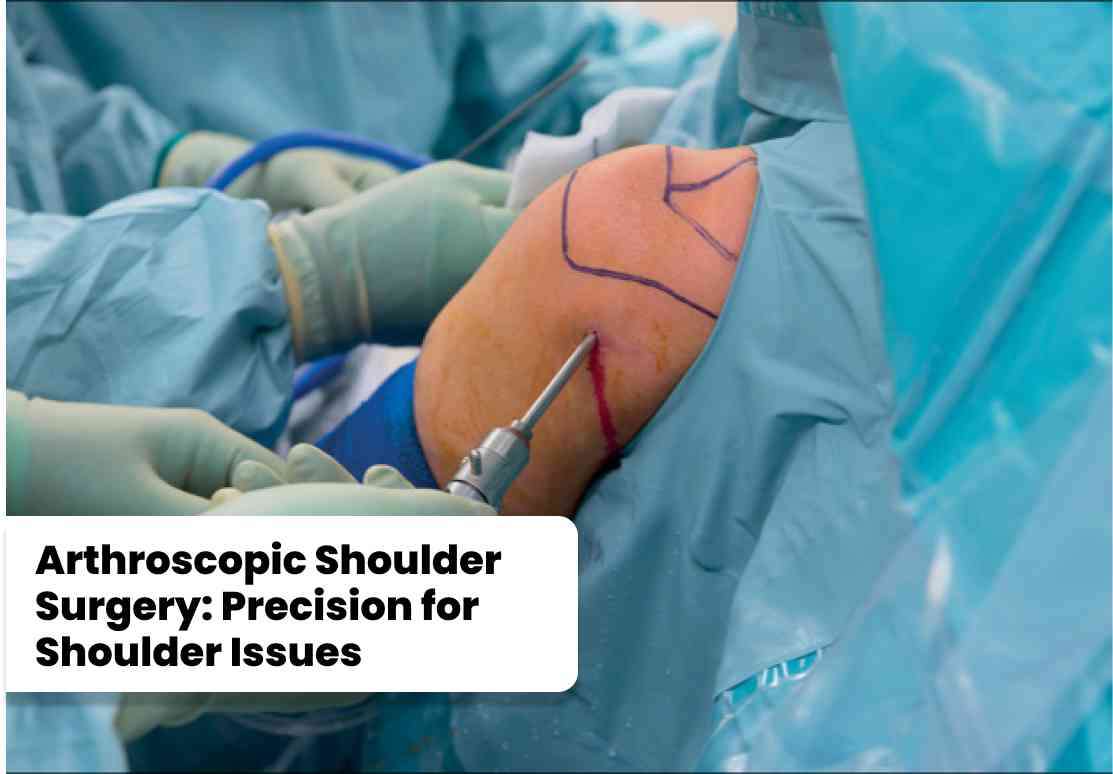
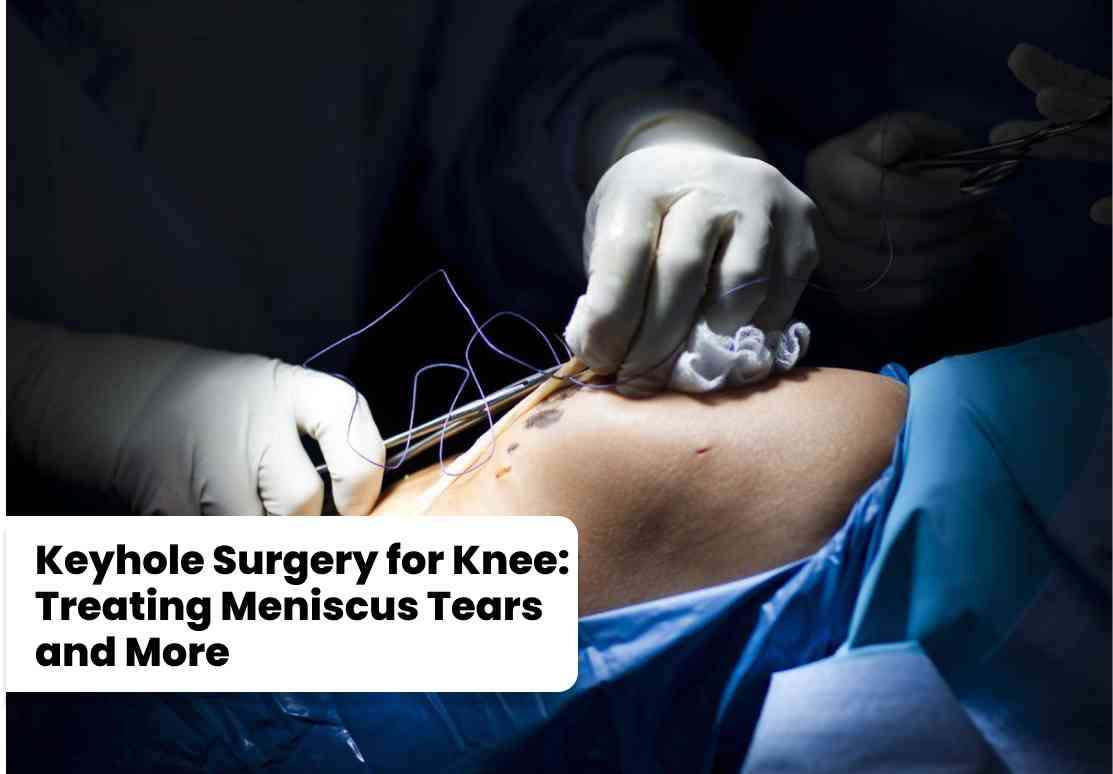
Laparoscopic knee surgery, another term for arthroscopy, is a minimally invasive procedure that provides a clear view of the interior of the knee joint. This technique is particularly effective for performing diagnostic arthroscopy, enabling surgeons to identify the root cause of knee pain or dysfunction. Subsequently, the same procedure can be utilized for various surgical interventions, such as debridement (removal of damaged tissue), ACL reconstruction, or Bankart repair for shoulder instability.
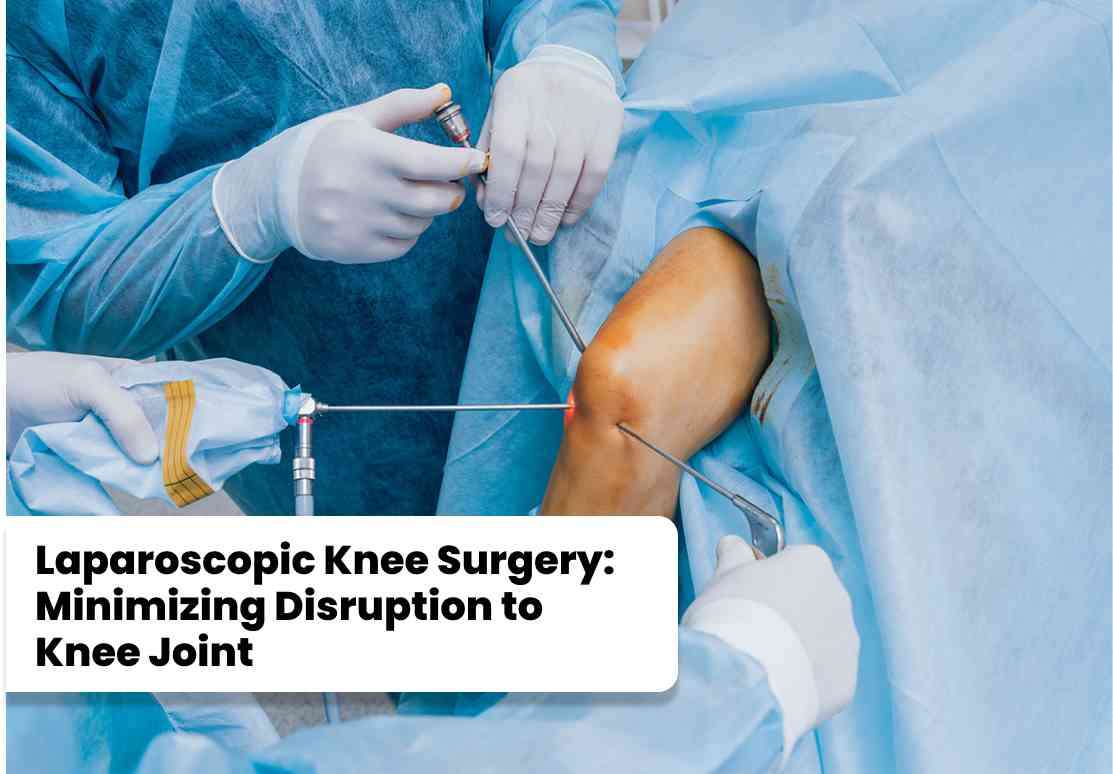
Laparoscopic knee surgery, another term for arthroscopy, is a minimally invasive procedure that provides a clear view of the interior of the knee joint. This technique is particularly effective for performing diagnostic arthroscopy, enabling surgeons to identify the root cause of knee pain or dysfunction. Subsequently, the same procedure can be utilized for various surgical interventions, such as debridement (removal of damaged tissue), ACL reconstruction, or Bankart repair for shoulder instability.
Arthroscopy offers numerous advantages over traditional open surgery. Firstly, the minimally invasive nature of arthroscopic procedures leads to smaller incisions, resulting in reduced scarring and a decreased risk of complications such as infection. Moreover, patients generally experience less postoperative pain and enjoy quicker recovery times, allowing them to return to their daily activities and sports sooner than with open surgery.

Arthroscopy offers numerous advantages over traditional open surgery. Firstly, the minimally invasive nature of arthroscopic procedures leads to smaller incisions, resulting in reduced scarring and a decreased risk of complications such as infection. Moreover, patients generally experience less postoperative pain and enjoy quicker recovery times, allowing them to return to their daily activities and sports sooner than with open surgery.
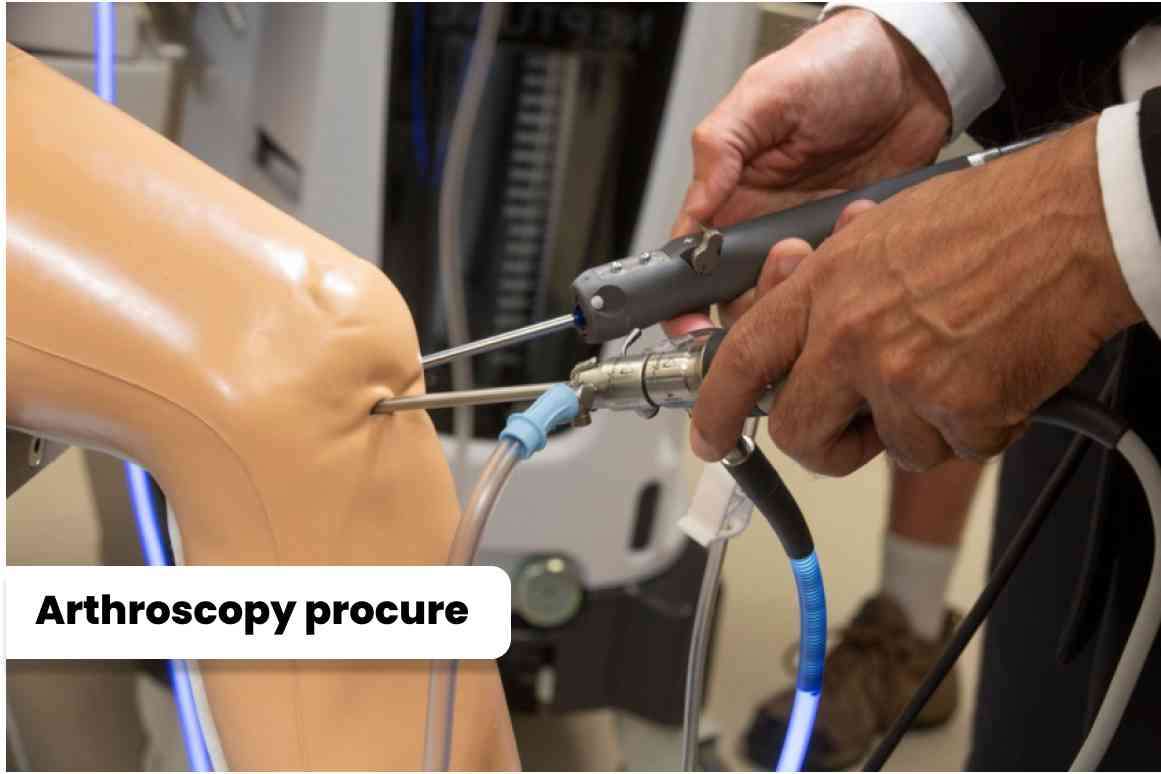
Here is a general overview of the arthroscopic
surgery procedure:
1. Anesthesia: The patient is given
anesthesia, which can be either local anesthesia (numbing only the surgical
area) or general anesthesia (putting the patient to sleep). 2. Incisions: The surgeon makes a few small
incisions (usually about ¼ to ½ inch long) near the joint being treated. These
incisions serve as entry points for the arthroscope and surgical instruments. 3. Arthroscope Insertion: The arthroscope is
inserted into one of the incisions. It consists of a tiny camera attached to a
flexible tube, allowing the surgeon to visualize the joint's interior on a
monitor. 4. Inspection and Diagnosis: The surgeon
carefully examines the joint structures, including the cartilage, ligaments,
tendons, and bones, using the arthroscope. This helps in diagnosing the problem
accurately. 5. Surgical Treatment: Depending on the specific
condition, the surgeon may perform various surgical procedures using
specialized instruments inserted through the other incisions. Examples include
removing damaged cartilage or loose bodies, repairing torn ligaments or
tendons, or smoothing rough joint surfaces. 6. Closure: Once the surgical procedure is
completed, the instruments are removed, and the incisions are closed. In some
cases, absorbable sutures or adhesive strips are used to close the incisions.
No stitches may be needed if the incisions are small enough. 7. Recovery: The patient is moved to a
recovery area, where they are monitored as they wake up from anesthesia. Pain
medications and instructions for post-operative care, including physical
therapy exercises, are provided. Arthroscopic surgery offers several advantages
over traditional open surgery, including smaller incisions, less tissue damage,
reduced scarring, faster recovery, and potentially fewer complications.
However, it's important to note that each case is unique, and the specific
details of the procedure may vary depending on the joint being treated and the
individual patient's condition. It is always best to consult with a qualified
orthopedic surgeon for detailed information and personalized advice.
Here is a general overview of the arthroscopic
surgery procedure:
1. Anesthesia: The patient is given
anesthesia, which can be either local anesthesia (numbing only the surgical
area) or general anesthesia (putting the patient to sleep). 2. Incisions: The surgeon makes a few small
incisions (usually about ¼ to ½ inch long) near the joint being treated. These
incisions serve as entry points for the arthroscope and surgical instruments. 3. Arthroscope Insertion: The arthroscope is
inserted into one of the incisions. It consists of a tiny camera attached to a
flexible tube, allowing the surgeon to visualize the joint's interior on a
monitor. 4. Inspection and Diagnosis: The surgeon
carefully examines the joint structures, including the cartilage, ligaments,
tendons, and bones, using the arthroscope. This helps in diagnosing the problem
accurately. 5. Surgical Treatment: Depending on the specific
condition, the surgeon may perform various surgical procedures using
specialized instruments inserted through the other incisions. Examples include
removing damaged cartilage or loose bodies, repairing torn ligaments or
tendons, or smoothing rough joint surfaces. 6. Closure: Once the surgical procedure is
completed, the instruments are removed, and the incisions are closed. In some
cases, absorbable sutures or adhesive strips are used to close the incisions.
No stitches may be needed if the incisions are small enough. 7. Recovery: The patient is moved to a
recovery area, where they are monitored as they wake up from anesthesia. Pain
medications and instructions for post-operative care, including physical
therapy exercises, are provided. Arthroscopic surgery offers several advantages
over traditional open surgery, including smaller incisions, less tissue damage,
reduced scarring, faster recovery, and potentially fewer complications.
However, it's important to note that each case is unique, and the specific
details of the procedure may vary depending on the joint being treated and the
individual patient's condition. It is always best to consult with a qualified
orthopedic surgeon for detailed information and personalized advice.
|
Serial No |
City |
Minimum Cost (INR) |
Average Cost (INR) |
|
1 |
Mumbai |
40,000 |
1,00,000 |
|
2 |
Delhi |
35,000 |
90,000 |
|
3 |
Bangalore |
30,000 |
80,000 |
|
4 |
Chennai |
30,000 |
75,000 |
|
5 |
Kolkata |
25,000 |
70,000 |
|
6 |
Hyderabad |
25,000 |
70,000 |
|
7 |
Pune |
25,000 |
65,000 |
|
8 |
Ahmedabad |
22,000 |
60,000 |
|
9 |
Jaipur |
20,000 |
55,000 |
|
10 |
Chandigarh |
20,000 |
55,000 |
|
11 |
Lucknow |
18,000 |
50,000 |
|
12 |
Indore |
18,000 |
50,000 |
|
13 |
Kochi |
16,000 |
45,000 |
|
14 |
Coimbatore |
16,000 |
45,000 |
|
15 |
Bhopal |
14,000 |
40,000 |
|
16 |
Nagpur |
14,000 |
40,000 |
|
17 |
Goa |
12,000 |
35,000 |
|
18 |
Mangalore |
12,000 |
35,000 |
|
19 |
Trivandrum |
12,000 |
30,000 |
|
20 |
Guwahati |
10,000 |
25,000 |
|
Serial No |
Hospital Name |
Address |
Contact Number |
|
1 |
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) |
Ansari Nagar, Aurobindo Marg, New Delhi - 110029 |
+91-11-26588500 |
|
2 |
Safdarjung Hospital |
Safdarjung Campus, Ansari Nagar, New Delhi - 110029 |
+91-11-26165060 |
|
3 |
Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER) |
Sector-12, Chandigarh - 160012 |
+91-172-2747585 |
|
4 |
King George's Medical University (KGMU) |
Chowk, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh - 226003 |
+91-522-2257450 |
|
5 |
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) |
Saket Nagar, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh - 462020 |
+91-755-2672355 |
|
6 |
Nizam's Institute of Medical Sciences (NIMS) |
Punjagutta, Hyderabad, Telangana - 500082 |
+91-40-23489000 |
|
7 |
Government Medical College and Hospital (GMCH) |
Sector 32, Chandigarh - 160030 |
+91-172-2601023 |
|
8 |
Institute of Medical Sciences (IMS), Banaras Hindu University (BHU) |
Lanka, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh - 221005 |
+91-542-2367568 |
|
9 |
Osmania General Hospital |
Afzal Gunj, Hyderabad, Telangana - 500012 |
+91-40-24600146 |
|
10 |
Government Medical College and Hospital (GMCH) |
Sector 32, Chandigarh - 160030 |
+91-172-2601023 |
Please Wait..