A fistula is an abnormal connection or passageway between two organs or
structures in the body. Fistulas can occur in various areas, such as the
digestive tract, urinary tract, or reproductive organs.
Call us to book an appointment with the best Proctology specialist near you.
Rectovaginal Fistula Treatment and VAAFT: Rectovaginal fistulas, which create an
abnormal connection between the rectum and vagina, require specialized
treatment. Surgical intervention, such as the use of the Video-Assisted Anal
Fistula Treatment (VAAFT), has gained prominence in recent years. VAAFT is a
minimally invasive procedure that uses a small endoscope to visualize and treat
the fistula tract. This technique offers the advantages of reduced
post-operative pain, shorter recovery time, and minimal scarring. Fibrin Glue Fistula Treatment and DLPL
Surgery: In some cases, fibrin glue can be used as an
alternative treatment for fistulas. Fibrin glue is a biological adhesive that
is applied to the fistula tract to promote closure. It works by stimulating the
body's natural healing process. This approach is particularly effective for
select types of fistulas, such as those in the digestive system.
Another surgical technique used for fistula
treatment is the Distal Ligation Proximal Laser (DLPL) procedure. DLPL surgery
involves the use of laser energy to close off the fistula tract, promoting
healing. This technique offers the advantage of being less invasive compared to
traditional open surgeries. Fistula Remedies and Thread Treatment: Apart from surgical options, there are
alternative remedies available for fistula treatment. Some individuals may find
relief through non-surgical approaches, such as herbal remedies or dietary
changes. However, it is important to note that the effectiveness of these
remedies may vary, and it is crucial to consult with healthcare professionals before
pursuing such options. Fistula Thread Treatment, also known as Kshar
Sutra, is a traditional Indian method that involves inserting a medicated
thread into the fistula tract. This thread gradually cuts and heals the fistula
over time. While this approach has shown promise in certain cases, it requires
skilled practitioners and may not be suitable for all types of fistulas. Fistula Treatment Without Surgery: In recent years, there has been growing
interest in non-surgical treatments for fistulas. Some studies have explored
the use of medications, such as antibiotics or immunosuppressants, to manage
fistula symptoms and promote healing. However, it is important to note that
non-surgical treatments may not be effective for all types of fistulas and should
be evaluated on a case-by-case basis. Fistula Medicine and Future Directions: Research in the field of fistula treatment
continues to advance, offering hope for improved outcomes. Scientists are
investigating new medications and therapies that target the underlying causes
of fistula formation, aiming to provide more effective and less invasive
treatment options in the future. While
some fistulas may heal on their own, others may require medical intervention.
Medications, surgery, fistula laser treatment, and colostomy or ileostomy are
some of the most common treatment options for fistulas. It is important to
consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate
treatment plan for fistulas.
Rectovaginal Fistula Treatment and VAAFT: Rectovaginal fistulas, which create an abnormal connection between the rectum and vagina, require specialized treatment. Surgical intervention, such as the use of the Video-Assisted Anal Fistula Treatment (VAAFT), has gained prominence in recent years. VAAFT is a minimally invasive procedure that uses a small endoscope to visualize and treat the fistula tract. This technique offers the advantages of reduced post-operative pain, shorter recovery time, and minimal scarring.
Fibrin Glue Fistula Treatment and DLPL Surgery: In some cases, fibrin glue can be used as an alternative treatment for fistulas. Fibrin glue is a biological adhesive that is applied to the fistula tract to promote closure. It works by stimulating the body's natural healing process. This approach is particularly effective for select types of fistulas, such as those in the digestive system.
Another surgical technique used for fistula treatment is the Distal Ligation Proximal Laser (DLPL) procedure. DLPL surgery involves the use of laser energy to close off the fistula tract, promoting healing. This technique offers the advantage of being less invasive compared to traditional open surgeries.
Fistula Remedies and Thread Treatment:
Apart from surgical options, there are alternative remedies available for fistula treatment. Some individuals may find relief through non-surgical approaches, such as herbal remedies or dietary changes. However, it is important to note that the effectiveness of these remedies may vary, and it is crucial to consult with healthcare professionals before pursuing such options.
Fistula Thread Treatment, also known as Kshar Sutra, is a traditional Indian method that involves inserting a medicated thread into the fistula tract. This thread gradually cuts and heals the fistula over time. While this approach has shown promise in certain cases, it requires skilled practitioners and may not be suitable for all types of fistulas.
Fistula Treatment Without Surgery:
In recent years, there has been growing interest in non-surgical treatments for fistulas. Some studies have explored the use of medications, such as antibiotics or immunosuppressants, to manage fistula symptoms and promote healing. However, it is important to note that non-surgical treatments may not be effective for all types of fistulas and should be evaluated on a case-by-case basis.
Fistula Medicine and Future Directions:
Research in the field of fistula treatment continues to advance, offering hope for improved outcomes. Scientists are investigating new medications and therapies that target the underlying causes of fistula formation, aiming to provide more effective and less invasive treatment options in the future.
While some fistulas may heal on their own, others may require medical intervention. Medications, surgery, fistula laser treatment, and colostomy or ileostomy are some of the most common treatment options for fistulas. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan for fistulas.
Seton placement is a surgical procedure used to treat anal fistulas, which are abnormal channels that develop between the anal canal and the skin surrounding the anus. A seton is a thin, flexible thread-like material that is placed in the fistula tract to help drain the infection and promote healing. During the procedure, the surgeon makes a small incision in the skin surrounding the fistula tract and passes the seton through the tract. The seton is then tied in a loop and left in place for several weeks or months to allow the fistula tract to heal around it. The seton acts as a drain, allowing the infected fluid to escape, reducing the risk of abscess formation and promoting healing.
Seton placement is a surgical procedure used to treat anal fistulas, which are abnormal channels that develop between the anal canal and the skin surrounding the anus. A seton is a thin, flexible thread-like material that is placed in the fistula tract to help drain the infection and promote healing.
During the procedure, the surgeon makes a small incision in the skin surrounding the fistula tract and passes the seton through the tract. The seton is then tied in a loop and left in place for several weeks or months to allow the fistula tract to heal around it. The seton acts as a drain, allowing the infected fluid to escape, reducing the risk of abscess formation and promoting healing.
During the procedure, the surgeon first locates the internal opening of the fistula and inserts a specialized instrument called a fistula probe into the channel. The probe is then passed through the external opening of the fistula, creating a tract that is sized to fit the fistula plug. The fistula plug is then inserted into the tract and secured in place with stitches or an adhesive. The fistula plug is made of a biodegradable material, such as porcine intestinal submucosa or synthetic material, that promotes the growth of new tissue and blood vessels to seal the fistula tract. Over time, the plug is absorbed by the body, leaving behind a scar that helps to seal the fistula. The use of a fistula plug has been shown to have a high success rate in treating anal fistulas, particularly in patients with simple, uncomplicated fistulas. However, the success rate may be lower in patients with complex or recurrent fistulas. The procedure is typically performed under local or general anesthesia, depending on the patient's preference and the surgeon's recommendation. After the procedure, the patient may experience some pain or discomfort, which can be managed with pain medication. The surgeon will typically schedule a follow-up visit to monitor the healing process and to remove any stitches, if necessary.
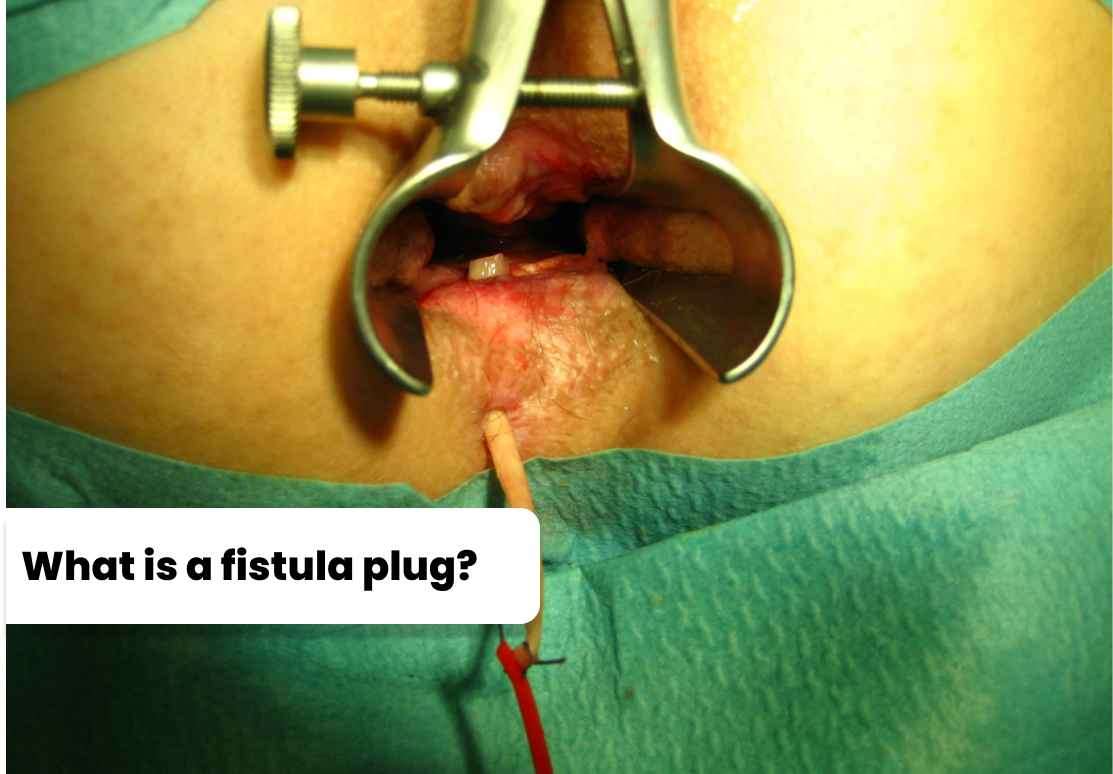
During the procedure, the surgeon first locates the internal opening of the fistula and inserts a specialized instrument called a fistula probe into the channel. The probe is then passed through the external opening of the fistula, creating a tract that is sized to fit the fistula plug. The fistula plug is then inserted into the tract and secured in place with stitches or an adhesive.
The fistula plug is made of a biodegradable material, such as porcine intestinal submucosa or synthetic material, that promotes the growth of new tissue and blood vessels to seal the fistula tract. Over time, the plug is absorbed by the body, leaving behind a scar that helps to seal the fistula.
The use of a fistula plug has been shown to have a high success rate in treating anal fistulas, particularly in patients with simple, uncomplicated fistulas. However, the success rate may be lower in patients with complex or recurrent fistulas. The procedure is typically performed under local or general anesthesia, depending on the patient's preference and the surgeon's recommendation.
After the procedure, the patient may experience some pain or discomfort, which can be managed with pain medication. The surgeon will typically schedule a follow-up visit to monitor the healing process and to remove any stitches, if necessary.
|
Serial No |
City |
Minimum Cost (INR) |
Average Cost (INR) |
|
1 |
Mumbai |
50,000 |
1,50,000 |
|
2 |
Delhi |
40,000 |
1,30,000 |
|
3 |
Bangalore |
35,000 |
1,20,000 |
|
4 |
Chennai |
30,000 |
1,10,000 |
|
5 |
Kolkata |
25,000 |
1,00,000 |
|
6 |
Hyderabad |
25,000 |
1,00,000 |
|
7 |
Pune |
20,000 |
90,000 |
|
8 |
Ahmedabad |
18,000 |
80,000 |
|
9 |
Jaipur |
18,000 |
80,000 |
|
10 |
Chandigarh |
15,000 |
70,000 |
|
11 |
Lucknow |
15,000 |
70,000 |
|
12 |
Indore |
12,000 |
60,000 |
|
13 |
Kochi |
12,000 |
60,000 |
|
14 |
Coimbatore |
10,000 |
50,000 |
|
15 |
Bhopal |
10,000 |
50,000 |
|
16 |
Nagpur |
8,000 |
45,000 |
|
17 |
Goa |
8,000 |
45,000 |
|
18 |
Mangalore |
6,000 |
40,000 |
|
19 |
Trivandrum |
6,000 |
40,000 |
|
20 |
Guwahati |
5,000 |
35,000 |
|
Serial No |
Hospital Name |
Address |
Contact Number |
|
1 |
All India Institute of |
Ansari Nagar, Aurobindo Marg, New Delhi - 110029 |
+91-11-26588500 |
|
2 |
Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education |
Sector-12, Chandigarh - 160012 |
+91-172-2747585 |
|
3 |
Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences (SGPGIMS) |
Rae Bareli Road, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh - 226014 |
+91-522-2668700 |
|
4 |
JIPMER (Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research) |
Dhanvantari Nagar, Puducherry - 605006 |
+91-413-2296000 |
|
5 |
Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology (SCTIMST) |
Medical College P.O., Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala - 695011 |
+91-471-2524266 |
|
6 |
King George's Medical University (KGMU) |
Chowk, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh - 226003 |
+91-522-2257450 |
|
7 |
Nizam's Institute of Medical Sciences (NIMS) |
Punjagutta, Hyderabad, Telangana - 500082 |
+91-40-23489000 |
|
8 |
Government Medical College and Hospital (GMCH) |
Sector 32, Chandigarh - 160030 |
+91-172-2601023 |
|
9 |
Institute of Medical Sciences (IMS), Banaras Hindu University (BHU) |
Lanka, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh - 221005 |
+91-542-2367568 |
|
10 |
Osmania General Hospital |
Afzal Gunj, Hyderabad, Telangana - 500012 |
+91-40-24600146 |
Please Wait..